目录
Arrays
Arrays类提供的的常见方法
用法示例
Comparable、Comparator
Comparable
Comparator
本篇学习Arrays,不算作是重点知识,但是为学习后面的Lambda表达式打一个基础,或者说,作为铺垫。
Arrays
- 用来操作数组的一个工具类。
Arrays类提供的的常见方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public static String toString(类型[] arr) | 返回数组的内容 |
| public static int[] copyOfRange(类型[] arr,起始索引,结束索引) | 拷贝数组(指定范围) |
| public static copyOf(类型[] arr, int newLength) | 拷贝数组 |
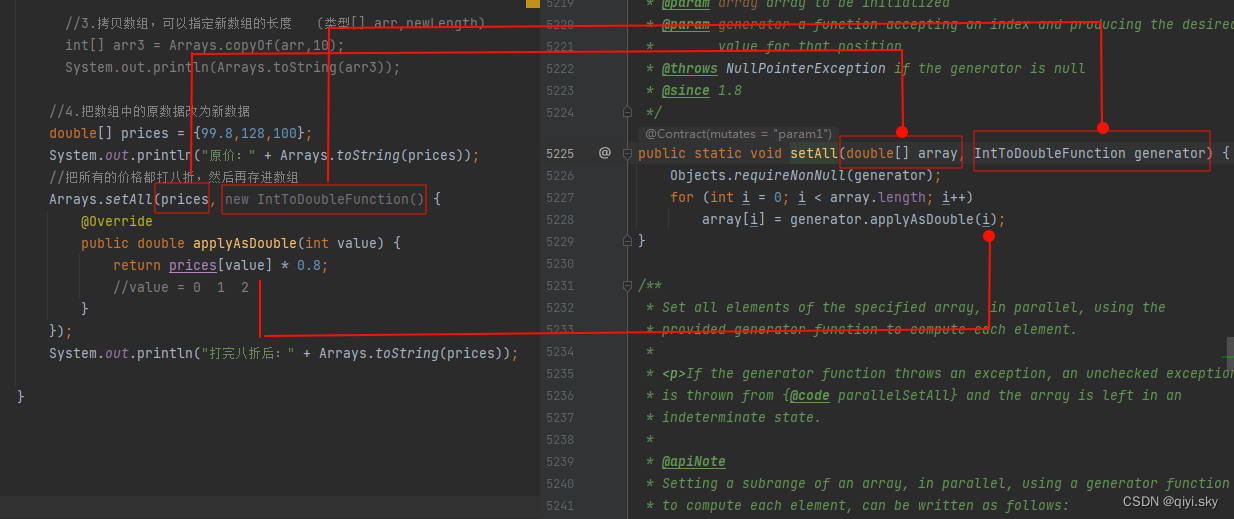
| public static setAll(double[] array, IntToDoubleFunction generator) | 把数组中的原数据改为新数据 |
| public static void sort(类型[] arr) | 对数组进行排序(默认是升序排序) |
用法示例
public static String toString(类型[] arr)
//1.toString返回数组的内容
int[] arr = new int[]{10,20,30,40,50,60};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));![]()
public static int[] copyOfRange(类型[] arr,起始索引,结束索引)
int[] arr = new int[]{10,20,30,40,50,60};//2.拷贝数组 (类型[] arr,起始索引,结束索引) 索引包前不包后
int[] arr2 = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr,1,4);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
public static copyOf(类型[] arr, int newLength)
int[] arr = new int[]{10,20,30,40,50,60};//3.拷贝数组,可以指定新数组的长度 (类型[] arr,newLength)
int[] arr3 = Arrays.copyOf(arr,10);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr3));
public static setAll(double[] array, IntToDoubleFunction generator)
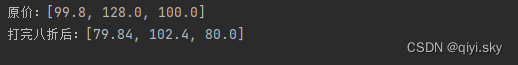
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args){//4.把数组中的原数据改为新数据double[] prices = {99.8,128,100};System.out.println("原价:" + Arrays.toString(prices));//把所有的价格都打八折,然后再存进数组Arrays.setAll(prices, new IntToDoubleFunction() {@Overridepublic double applyAsDouble(int value) {return prices[value] * 0.8;//value = 0 1 2}});System.out.println("打完八折后:" + Arrays.toString(prices));}
}
运行结果:
看setAll的源码:
public static void sort(类型[] arr)
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args){//4.把数组中的原数据改为新数据double[] prices = {99.8,128,100};System.out.println("排序前:" + Arrays.toString(prices));//5.对数组进行排序(默认是升序排序)Arrays.sort(prices);System.out.println("排序后:" + Arrays.toString(prices));}
}
运行结果:

Comparable、Comparator
如果数组中存储的是对象,那该如何排序呢?
Arrays.sort中没有指定对于对象的排序规则,不知道根据什么来排序,所以如果用它来对对象排序的话是会报错的。
解决方式
- 方式一:让该对象的类实现Comparable(比较规则)接口,然后重写compareTo方法,自己来制定比较规则。
- 方式二:使用下面这个sort方法,创建Comparator比较器接口的匿名内部类对象,然后自己制定比较规则。
public static<T>void sort(T[]arr,Comparator<?super T>c)
//对数组进行排序(支持自定义排序规则)我们来看方式一:实现Comparable接口
Comparable
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args){Student[] students = new Student[4];students[0] = new Student("蜘蛛精",169.5,24);students[1] = new Student("紫霞",163.8,25);students[2] = new Student("紫霞",163.8,25);students[3] = new Student("至尊宝",167.5,21);//1.对数组进行排序Arrays.sort(students);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(students));}
}
package user.APITest;public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{private String name;private double height;private int age;//制定比较规则//假设this 与 o 进行比较@Overridepublic int compareTo(Student o) {//约定1:认为左边对象 大于 右边对象,则要返回正整数//约定2:认为左边对象 小于 右边对象,则要返回负整数//约定3:认为左边对象 等于 右边对象,则要返回0//按照年龄升序排序if(this.age > o.age){return 1;}else if(this.age < o.age){return -1;}return 0;}//重写toString方法@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", height=" + height +", age=" + age +'}';}public Student() {}public Student(String name, double height, int age) {this.name = name;this.height = height;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public double getHeight() {return height;}public void setHeight(double height) {this.height = height;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}
}
通过让对象的类实现Comparable接口并且重写compareTo方法,可以自定义排序规则,对对象数组进行排序,运行结果:

注意:这里制定排序规则,我们可以换一下编码思路,改得更简洁一点
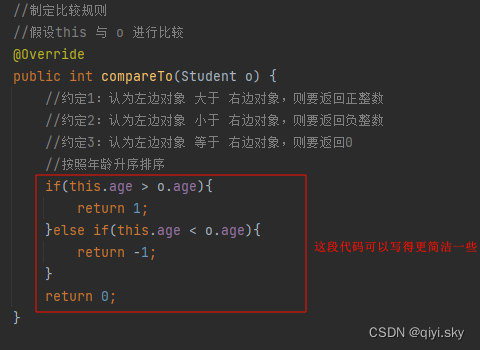
例如:
//制定比较规则//假设this 与 o 进行比较@Overridepublic int compareTo(Student o) {//约定1:认为左边对象 大于 右边对象,则要返回正整数//约定2:认为左边对象 小于 右边对象,则要返回负整数//约定3:认为左边对象 等于 右边对象,则要返回0//按照年龄升序排序
// if(this.age > o.age){
// return 1;
// }else if(this.age < o.age){
// return -1;
// }
// return 0;return this.age - o.age;}如果要将升序排序改为降序,那调换一下位置即可:
return o.age - this.age;也就是原本this > o,按升序进行相减时返回正整数;那么换位置进行相减得到负整数,从原本认为this > o的改为了o > this。也就是说,返回负整数,证明左边对象this 小于 右边对象o。
接下来再看方式二:Comparator
Comparator
现在来排序Student类里面的身高,方式二实际上是调用sort的重载方法,其参数需要传入该对象以及Comparator比较器接口的匿名内部类对象。
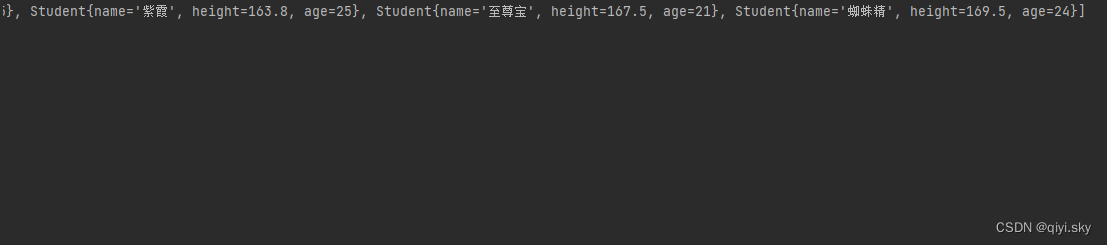
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args){Student[] students = new Student[4];students[0] = new Student("蜘蛛精",169.5,24);students[1] = new Student("紫霞",163.8,25);students[2] = new Student("紫霞",163.8,25);students[3] = new Student("至尊宝",167.5,21);//2.方式二:创建Comparator比较器接口的匿名内部类对象,然后自己制定比较规则。Arrays.sort(students, new Comparator<Student>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {//制定比较规则//o1 o2//这里的规则是与前面一模一样的//约定1:认为左边对象 大于 右边对象,则要返回正整数//约定2:认为左边对象 小于 右边对象,则要返回负整数//约定3:认为左边对象 等于 右边对象,则要返回0//根据身高排序//return o1.getHeight() - o2.getHeight(); //这里就不能使用之前那种编码方式了,不能保证相减得到的正整数是准确的结果//先来看第一种: 升序if(o1.getHeight() > o2.getHeight()){return 1;}else if(o1.getHeight() < o2.getHeight()){return -1;}return 0;}});System.out.println(Arrays.toString(students));}
}
运行结果:
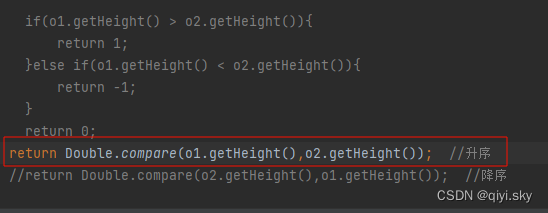
将排序规则的编码简化:
下篇就要学习Lambda表达式,对匿名内部类进行简化。
END
学习自:黑马程序员——JavaSE课程