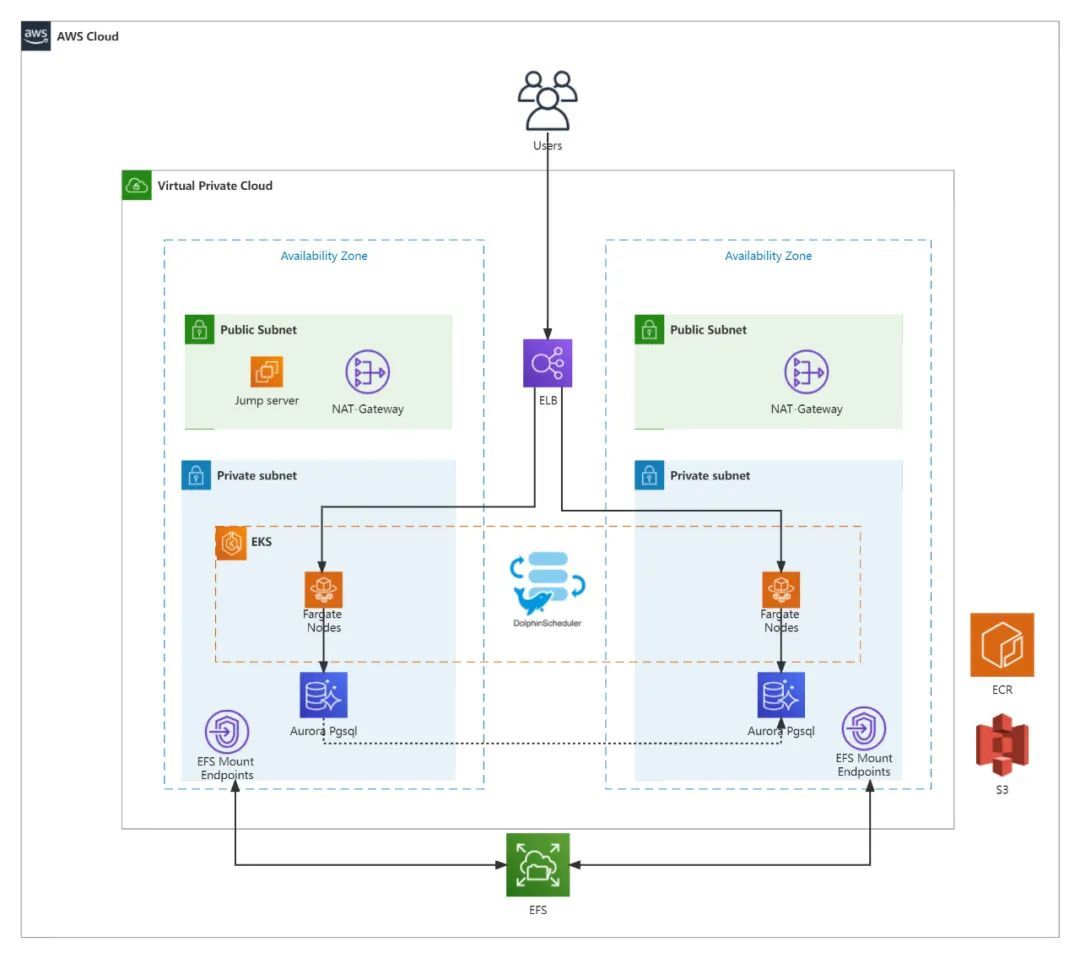
VPC (Virtual Private Cloud):
参考:https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpc/latest/userguide/what-is-amazon-vpc.html
With Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC), you can launch AWS resources in a logically isolated virtual network that you’ve defined. This virtual network closely resembles a traditional network that you’d operate in your own data center, with the benefits of using the scalable infrastructure of AWS.
The following diagram shows an example VPC. The VPC has one subnet in each of the Availability Zones in the Region, EC2 instances in each subnet, and an internet gateway to allow communication between the resources in your VPC and the internet.

VPC Peering
参考: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpc/latest/peering/what-is-vpc-peering.html
A VPC peering connection is a networking connection between two VPCs that enables you to route traffic between them using private IPv4 addresses or IPv6 addresses. Instances in either VPC can communicate with each other as if they are within the same network. You can create a VPC peering connection between your own VPCs, or with a VPC in another AWS account. The VPCs can be in different Regions (also known as an inter-Region VPC peering connection).
AWS uses the existing infrastructure of a VPC to create a VPC peering connection; it is neither a gateway nor a VPN connection, and does not rely on a separate piece of physical hardware. There is no single point of failure for communication or a bandwidth bottleneck.
A VPC peering connection helps you to facilitate the transfer of data. For example, if you have more than one AWS account, you can peer the VPCs across those accounts to create a file sharing network. You can also use a VPC peering connection to allow other VPCs to access resources you have in one of your VPCs.

PrivateLink
参考:https://www.megaport.com/blog/aws-privatelink-explained/
PrivateLink is a networking construct that allows an application/service residing in one VPC (the “Service Provider VPC”) to be accessed by clients/consumers in (or through) other VPCs within the AWS Region (“Consumer VPCs”).
The consumer accesses the service privately via an interface (VPC Endpoint) deployed locally in the Consumer VPC, avoiding any requirement for internet connectivity and keeping all traffic inside AWS’s private network.
Importantly, the Service Provider VPC and the consumer VPCs can be owned by different AWS accounts.

VPC endpoints
VPC endpoints are resources that can be deployed into a VPC to serve as a path through which to access various services. Part of the VPC endpoint functionality forms part of PrivateLink.
There are 3 types of VPC endpoints:
- Interface endpoint - this is the type used by PrivateLink. It is a network interface with an IP address that sits inside the VPC subnet, and requests are made either directly to this IP or more commonly to a DNS name that resolves to this IP. PrivateLink then transparently sends these requests to the backend (the service provider) and returns the response.
- Gateway endpoint - this type of endpoint attaches to the VPC in a similar fashion to an Internet Gateway (IGW) or Virtual Gateway (VGW). It doesn’t appear as an IP within your VPC, but rather as a destination/target for routes in the VPC Route Table. Traffic to the IP addresses of the destination service is routed through the gateway endpoint. This type of endpoint is only available for S3 and DynamoDB (although you can also use an Interface Endpoint for those services), and can only be used by resources in the local VPC.
- Gateway Load Balancer endpoint - this type of VPC Endpoint is used to direct network traffic to a set of network virtual appliances (eg. firewalls) which are deployed using the Gateway Load Balancer service/architecture.
PrivateLink VS VPC Peerings
PrivateLink and VPC Peerings both provide a way to access resources in one VPC from another VPC, however, the method and use cases are quite different.
While PrivateLink creates a local interface with a local IP which allows unidirectional access to a specific application/port, VPC Peering creates a bidirectional layer 3 connection between two VPCs.
What this means is that PrivateLink allows consumers in one VPC to access a specific app in another VPC (with no traffic in the reverse direction), whereas VPC Peering allows all resources in two VPCs to talk to each other.
VPC Peering can also connect VPCs that are in different regions, where PrivateLink cannot. However, VPC Peering can be used in combination with PrivateLink to extend PrivateLink across regions.
Key Differences:
- Connectivity
AWS PrivateLink: Provides unidirectional access from consumers in one VPC to a specific application or service in another VPC through a local interface with a local IP.
VPC Peering: Establishes a bidirectional layer 3 connection between two VPCs, allowing all resources in both VPCs to communicate with each other. - Use Case
AWS PrivateLink: Ideal for exposing a specific service or application to consumers in another VPC while maintaining high security and isolation.
VPC Peering: Suitable for creating a fully-meshed network where multiple VPCs need to communicate directly with each other. - Architecture
AWS PrivateLink: Uses interface endpoints to create a private connection to the service, simplifying the access control and security.
VPC Peering: Requires the establishment of peering connections between each pair of VPCs, which can become complex as the number of VPCs increases. - Transitive Routing
AWS PrivateLink: Does not support transitive routing. Traffic is confined to the endpoint connection.
VPC Peering: Does not support transitive routing. Each VPC must be directly peered with every other VPC it needs to communicate with. - Network Connectivity
AWS PrivateLink: Limited to the AWS region where the VPCs reside, but can be extended across regions using VPC Peering.
VPC Peering: Supports both intra-region and inter-region connections, allowing VPCs in different regions to communicate directly. - Security
AWS PrivateLink: Provides enhanced security by isolating traffic within the AWS network and limiting exposure to a specific application or service.
VPC Peering: Ensures secure communication between VPCs without traversing the public internet, but exposes all resources in the peered VPCs to each other. - Complexity
AWS PrivateLink: Easier to set up for specific service access, with simplified access control.
VPC Peering: More complex to manage with an increasing number of VPCs due to the need for multiple peering connections.
Use Cases
- Choose AWS PrivateLink if:
You need to provide access to a specific application or service in another VPC.
You require unidirectional access to ensure tighter security controls.
You want to simplify the setup and management of network connections to a specific service. - Choose VPC Peering if:
You need full bidirectional communication between two or more VPCs.
Your architecture requires direct connectivity between all resources in the connected VPCs.
You are connecting VPCs across different regions and need direct communication paths.
ELB (Elastic Load Balancing)
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/elastic-load-balancer-in-aws/
The elastic load balancer is a service provided by Amazon in which the incoming traffic is efficiently and automatically distributed across a group of backend servers in a manner that increases speed and performance. It helps to improve the scalability of your application and secures your applications. Load Balancer allows you to configure health checks for the registered targets. In case any of the registered targets (Autoscaling group) fails the health check, the load balancer will not route traffic to that unhealthy target. Thereby ensuring your application is highly available and fault tolerant. To know more about load balancing refer to Load Balancing in Cloud Computing.
Types of Load Balancers:
- Classic Load Balancer
It is the traditional form of load balancer which was used initially. It distributes the traffic among the instances and is not intelligent enough to support host-based routing or path-based routing. It ends up reducing efficiency and performance in certain situations. It is operated on the connection level as well as the request level. Classic Load Balancer is in between the transport layer (TCP/SSL) and the application layer (HTTP/HTTPS). - Application Load Balancer
This type of Load Balancer is used when decisions are to be made related to HTTP and HTTPS traffic routing. It supports path-based routing and host-based routing. This load balancer works at the Application layer of the OSI Model. The load balancer also supports dynamic host port mapping. - Network Load Balancer
This type of load balancer works at the transport layer(TCP/SSL) of the OSI model. It’s capable of handling millions of requests per second. It is mainly used for load-balancing TCP traffic. - Gateway Load Balancer
Gateway Load Balancers provide you the facility to deploy, scale, and manage virtual appliances like firewalls. Gateway Load Balancers combine a transparent network gateway and then distribute the traffic.
Placement Group
To meet the needs of your workload, you can launch a group of interdependent EC2 instances into a placement group to influence their placement.
Depending on the type of workload, you can create a placement group using one of the following placement strategies:
-
Cluster Placement Group – Packs instances close together inside an Availability Zone. This strategy enables workloads to achieve the low-latency network performance necessary for tightly-coupled node-to-node communication that is typical of high-performance computing (HPC) applications.
-
Partition Placement Group – Spreads your instances across logical partitions such that groups of instances in one partition do not share the underlying hardware with groups of instances in different partitions. This strategy is typically used by large distributed and replicated workloads, such as Hadoop, Cassandra, and Kafka.
-
Spread Placement Group – Strictly places a small group of instances across distinct underlying hardware to reduce correlated failures.
Placement groups are optional. If you don’t launch your instances into a placement group, EC2 tries to place the instances in such a way that all of your instances are spread out across the underlying hardware to minimize correlated failures.