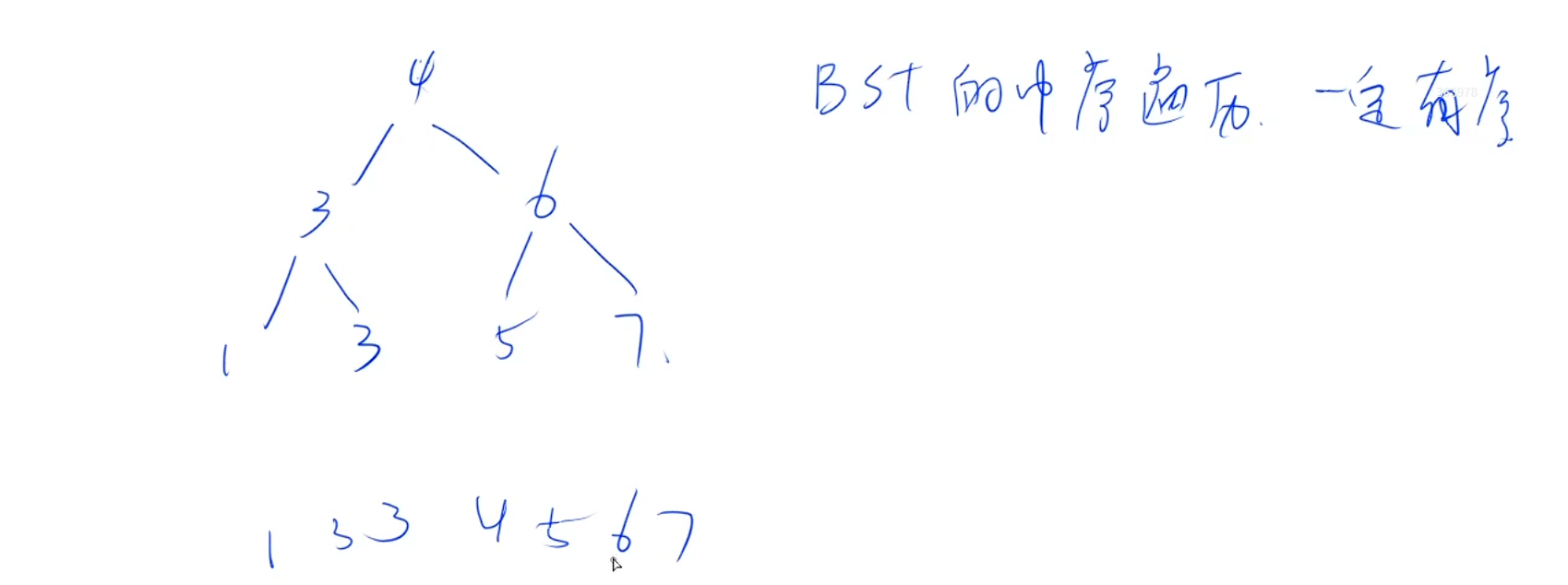
镜像后的树
样例是前序遍历,中序序列就是把前序序列sort一下,然后根据中序序列和前序序列构造一棵树,和树的遍历一样
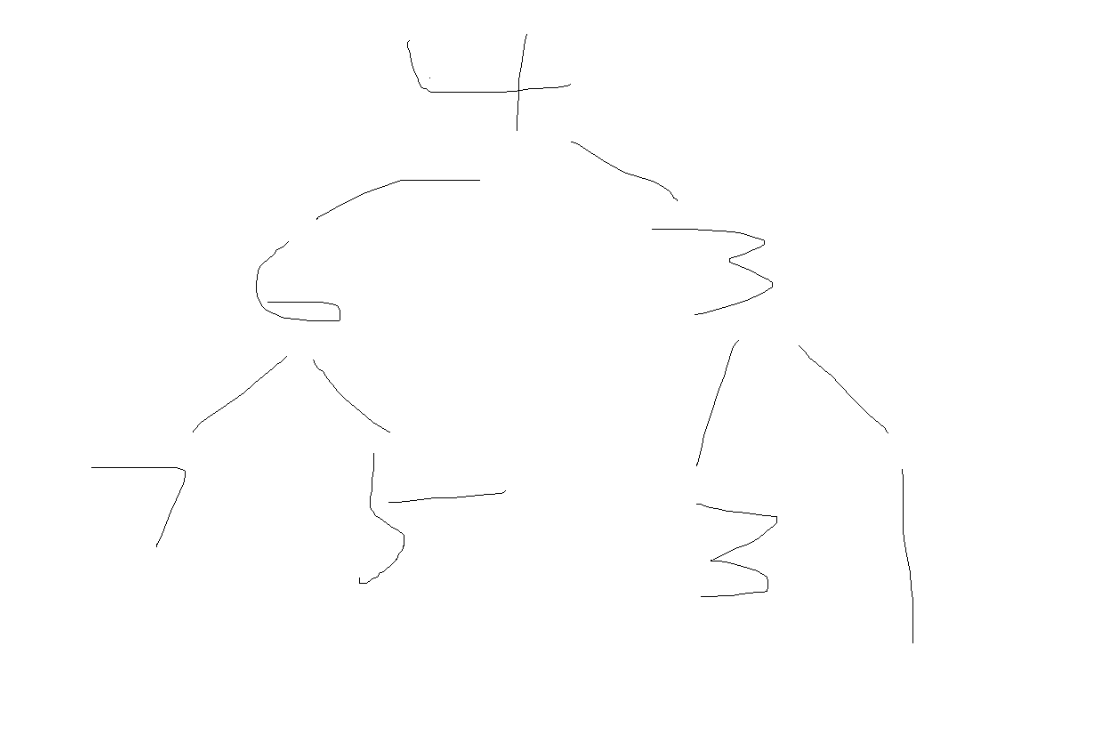
前序序列:8 6 5 7 10 8 11
中序序列:5 6 7 8 8 10 11
镜像后的中序序列:11 10 8 8 7 6 5
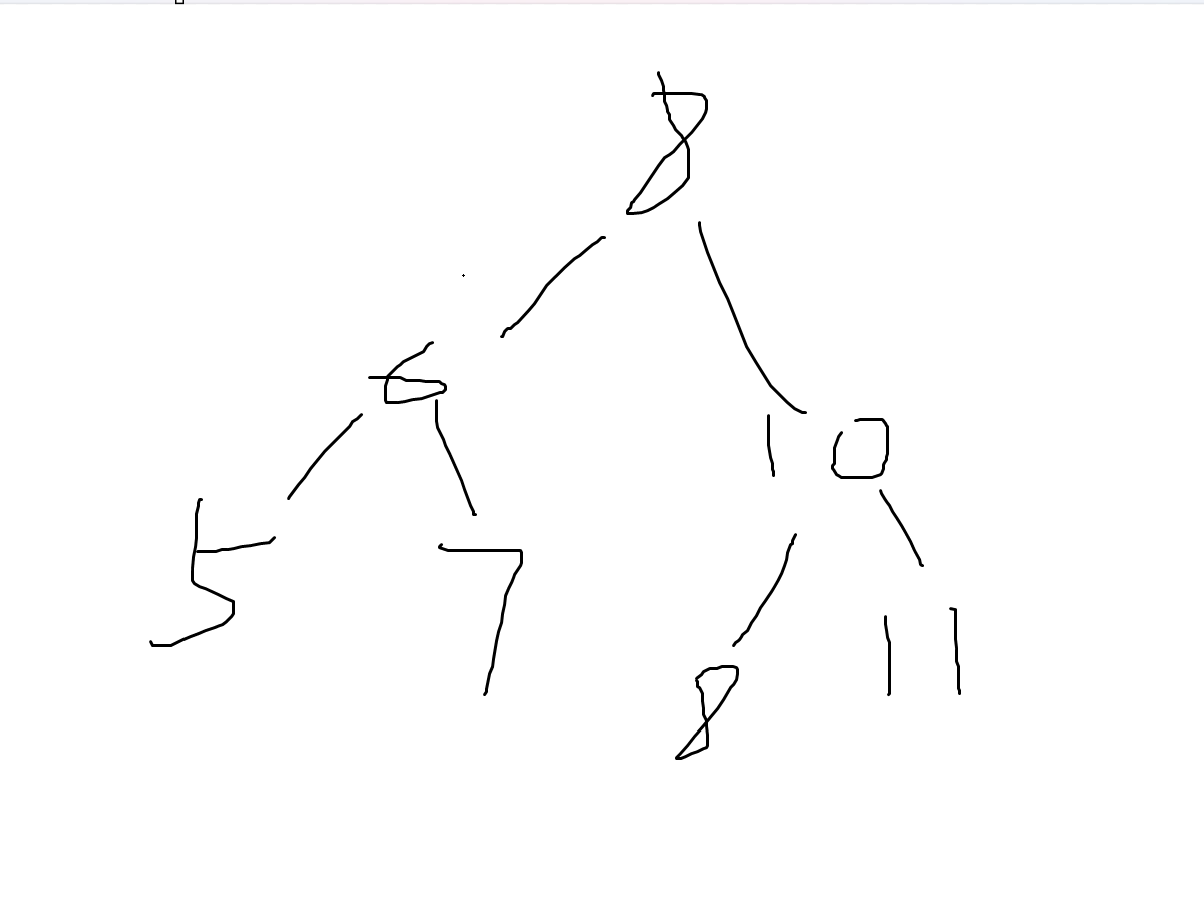
###在中序序列中有多个相同的根结点,取第一个
###如果在中序序列中找不到根结点,就代表不合法
###在镜像后的中序序列中有多个相同的根结点,取最后一个
做两遍BST和BST镜像后
镜像后就是把中序遍历反过来,右子树小于当前的根结点
注意思考回溯,遍历完左子树,再遍历右子树,最后是根结点
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>using namespace std;const int N = 1010;int n;
// 前序遍历 中序遍历
int preorder[N], inorder[N];
// 后序遍历 后序遍历存值用cnt
int postorder[N], cnt;
// 重建搜索二叉树 中序遍历左右边界 前序遍历左右边界 有无镜像
bool build(int il, int ir, int pl, int pr, int type)
{if (il > ir) return true; // 当前区间没有元素 一定重建成功// 根结点 前序遍历的第一个结点int root = preorder[pl];//找根结点在中序遍历的位置int k;if (type == 0) //原树 无镜像 从左向右找{for (k = il; k <= ir; k ++ )if (inorder[k] == root)break;//当循环结束时,k=ir+1,表示没找到if (k > ir) return false;}else //镜像 从右向左找{//从右往左找根结点在中序遍历的位置for (k = ir; k >= il; k -- )if (inorder[k] == root)break;if (k < il) return false;}bool res = true;// 后序遍历 先遍历两个子树 再遍历两个根结点if (!build(il, k - 1, pl + 1, pl + 1 + (k - 1 - il), type)) res = false;// 左子树重建不成功if (!build(k + 1, ir, pl + 1 + (k - 1 - il) + 1, pr, type)) res = false;// 右子树重建不成功// 将根结点遍历postorder[cnt ++ ] = root;//在进行上面的两次build时,已经把左子树和右子树放到了postorder中,左右根,现在把根节点放到postorder中return res;
}int main()
{cin >> n;for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ){cin >> preorder[i];inorder[i] = preorder[i];}// 前序遍历排序得到中序遍历sort(inorder, inorder + n);// 是原二叉搜索树的前序遍历 type == 0if (build(0, n - 1, 0, n - 1, 0)){puts("YES");// 输出后序遍历cout << postorder[0];for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++ ) cout << ' ' << postorder[i];cout << endl;}else // 原二叉搜索树没有重建成功{// 翻转得到镜像 reverse(inorder, inorder + n);cnt = 0;// 判断根据镜像能否重建二叉搜索树 type == 1if (build(0, n - 1, 0, n - 1, 1)){puts("YES");cout << postorder[0];for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++ ) cout << ' ' << postorder[i];cout << endl;}// 重建不成功 其不是二叉搜索树或其镜像进行前序遍历的结果else puts("NO");}return 0;
}

















![[GXYCTF2019]Ping Ping Ping1](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/ba497813864f4a318a5f65f9395636b0.png)
