在我自学C++过程中,我选择了C++Primer这本书,并对部分代码习题进行了求解以及运行结果。接下来几个月我将为大家定时按章节更新习题答案与运行结果,运行环境(Visual Studio Code,windows 11):
3.1.1.使用恰当的using 声明重做 1.4.1节和2.6.2节的练习。
1.4.1
#include <iostream>using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;int main()
{int sum = 0;for (int val = 1; val <= 10; ++val) sum += val;cout << "Sum of 1 to 10 inclusive is " << sum << endl;return 0;
}![]()
2.6.2
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std :: cin;
using std :: cout;
using std :: endl;
using std :: string;
struct Sale_data
{string bookNo;unsigned units_sold = 0;double revenue = 0.0;
};
int main()
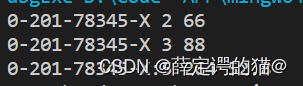
{Sale_data total;double totalprice;if(cin >> total.bookNo >> total.units_sold >> totalprice){total.revenue = total.units_sold*totalprice;Sale_data nextdata;double nextprice;while(cin >> nextdata.bookNo >> nextdata.units_sold >> nextprice){nextdata.revenue = nextprice*nextdata.units_sold;if(total.bookNo == nextdata.bookNo){total.units_sold += nextdata.units_sold;total.revenue += nextdata.revenue;}else{cout << total.bookNo << ":" << total.units_sold << " " << total.revenue << " ";if(total.units_sold != 0) cout << total.revenue/total.units_sold << endl;else cout << "No Sales!" << endl;total.bookNo = nextdata.bookNo;total.units_sold =nextdata.units_sold;total.revenue = nextdata.revenue;}}cout << total.bookNo << ":" << total.units_sold << " " << total.revenue << " ";if(total.units_sold != 0) cout << total.revenue/total.units_sold << endl;else cout << "No Sales!" << endl;}else cout << "No data!" << endl;return 0;
}
3.2.编写一段程序从标准输入中一次读入一行,然后修改该程序使其一次读入一个词。
One Row
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std :: cin;
using std :: cout;
using std :: endl;
using std :: string;
using std :: getline;
int main()
{string l;while(getline(cin,l)){cout << l << endl;}return 0;
}
One Word!
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std :: cin;
using std :: cout;
using std :: endl;
using std :: string;
int main()
{string w;while(cin >> w){cout << w << endl;}return 0;
}
3.4.编写一段程序读取两个字符串,比较其是否相等并输出结果。如果不相等,输出比较大的那个字符串。改写上述程序,比较输入的两个字符串是否等长,如果不等长,输出长度较大的那个字符串。
3.4.1
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std :: cin;
using std :: cout;
using std :: endl;
using std :: string;
int main()
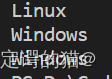
{string w1, w2;cin >> w1;cin >> w2;if(w1 == w2)cout << "相等!" << endl;else if(w1 > w2)cout << w1 << endl;elsecout << w2 << endl;return 0;
}
3.4.2
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std :: cin;
using std :: cout;
using std :: endl;
using std :: string;
int main()
{string w1, w2;cin >> w1;cin >> w2;if(w1.length() == w2.length())cout << "相等!" << endl;else if(w1.length() > w2.length())cout << w1 << endl;elsecout << w2 << endl;return 0;
}
3.5.编写一段程序从标准输入中读入多个字符串并将他们连接起来,输出连接成的大字符串。然后修改上述程序,用空格把输入的多个字符串分割开来。
3.5.1.字符串拼接
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std :: cin;
using std :: cout;
using std :: endl;
using std :: string;
int main()
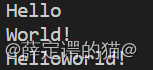
{string w1, w2, w;cin >> w1;cin >> w2;w = w1 + w2;cout << w << endl;return 0;
}
3.5.2.空格拼接。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std :: cin;
using std :: cout;
using std :: endl;
using std :: string;
int main()
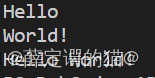
{string w1, w2, w;cin >> w1;cin >> w2;w = w1 + " " + w2;cout << w << endl;return 0;
}
3.6 编写一段程序,使用范围for语句将字符串内的所有字符用X代替。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>using std::string;
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;int main()
{string s = "Hello World!";for(auto &c : s)c = 'X';cout << s << endl;return 0;
}![]()
3.7 就上一题完成的程序而言,如果将循环控制变量的类型设为char将发生什么?先估计一下结果,然后实际编程进行验证。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>using std::string;
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;int main()
{string s = "Hello World!";for(char &c : s)c = 'X';cout << s << endl;return 0;
}![]()
3.8 分别用while循环和传统的for循环重写第一题的程序,你觉得哪种形式更好呢?为什么?
#include <iostream>
#include <string>using std::string;
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;int main()
{string s = "Hello World!";decltype (s.size()) i = 0;while(i != s.size()){s[i] = 'X';i++;}cout << s << endl;for(i = 0;i != s.size();i++){s[i] = 'X';}cout << s << endl;return 0;
}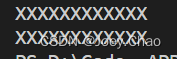
3.9 下面的程序有何作用?它合法吗?如果不合法,为什么?
string s;
cout << s[0] << endl;不合法。使用下标访问空字符串是非法行为。
3.10 编写一段程序,读入一个包含标点符号的字符串,将标点符号去除后输出字符串剩余的部分。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>using std::string;
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;int main()
{string s = "Hello , World!";string re;for(auto x : s){if(!ispunct(x))re = re + x;}cout << re << endl;return 0;
}![]()
3.14 编写一段程序,用cin读入一组整数并把它们存入一个vector对象。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::vector;int main()
{vector<int> v;int i;while (cin >> i){v.push_back(i);}return 0;
}
3.15 改写上题的程序,不过这次读入的是字符串。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::vector;
using std::string;int main()
{vector<string> v;string i;while (cin >> i){v.push_back(i);}return 0;
}
3.16 编写一段程序,把练习3.13中vector对象的容量和具体内容输出出来。检验你之前的回答是否正确,如果不对,回过头重新学习3.3.1节(第87页)直到弄明白错在何处为止。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::vector;
using std::string;int main()
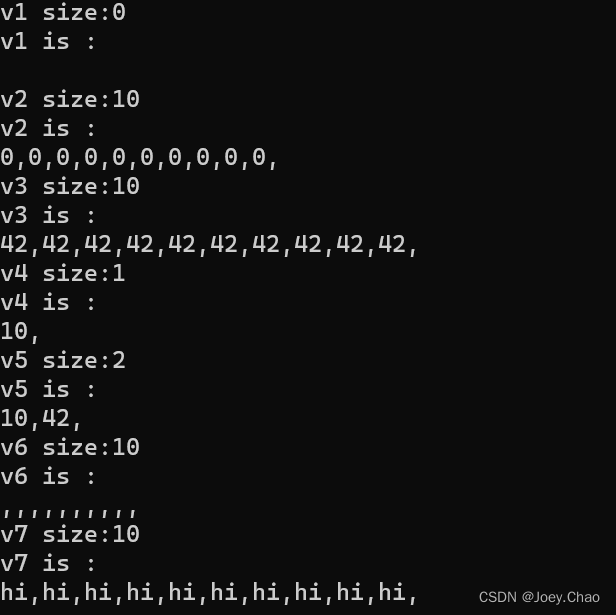
{vector<int> v1; vector<int> v2(10); vector<int> v3(10, 42); vector<int> v4{ 10 }; vector<int> v5{ 10, 42 }; vector<string> v6{ 10 }; vector<string> v7{ 10, "hi" };cout << "v1 size:" << v1.size() << endl;cout << "v1 is :" << endl;for (auto i : v1){cout << i << ",";}cout << endl;cout << "v2 size:" << v2.size() << endl;cout << "v2 is :" << endl;for (auto i : v2){cout << i << ",";}cout << endl;cout << "v3 size:" << v3.size() << endl;cout << "v3 is :" << endl;for (auto i : v3){cout << i << ",";}cout << endl;cout << "v4 size:" << v4.size() << endl;cout << "v4 is :" << endl;for (auto i : v4){cout << i << ",";}cout << endl;cout << "v5 size:" << v5.size() << endl;cout << "v5 is :" << endl;for (auto i : v5){cout << i << ",";}cout << endl;cout << "v6 size:" << v6.size() << endl;cout << "v6 is :" << endl;for (auto i : v6){cout << i << ",";}cout << endl;cout << "v7 size:" << v7.size() << endl;cout << "v7 is :" << endl;for (auto i : v7){cout << i << ",";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
3.17 从cin读入一组词并把它们存入一个vector对象,然后设法把所有词都改写为大写形式。输出改变后的结果,每个词占一行。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::vector;
using std::string;int main()
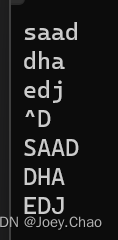
{vector<string> v;string s;while (cin >> s){v.push_back(s);}for (auto& c1 : v){for (auto& c2 : c1){c2 = toupper(c2);}}for (auto i : v){cout << i << endl;}return 0;
}
3.19 如果想定义一个含有10个元素的vector对象,所有元素的值都是42,请列举出三种不同的实现方法。哪种方法更好呢?为什么?
1:
vector<int> ivec1(10, 42);2:
vector<int> ivec2{ 42, 42, 42, 42, 42, 42, 42, 42, 42, 42 };3:
vector<int> ivec3;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)ivec3.push_back(42);方法1最好。
3.20 读入一组整数并把他们存入一个vector对象,将每对相邻整数的和输出出来。改写你的程序,这次要求先输出第一个和最后一个元素的和,接着输入第二个和倒数第二个元素的和,以此类推。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::vector;
using std::string;int main()
{vector<int> v0, v1, v2;int i;while (cin >> i){v0.push_back(i);}for (decltype(v0.size()) index = 0; index < v0.size(); index++){cout << v0[index] << " ";}cout << endl;for (decltype(v0.size()) index = 0; index < v0.size() - 1; index++){v1.push_back(v0[index] + v0[index + 1]);}for (decltype(v1.size()) index = 0; index < v1.size(); index++){cout << v1[index] << " ";}cout << endl;for (decltype(v0.size()) index = 0; index < v0.size() / 2 + 1 && index<= v0.size()-1-index; index++){v2.push_back(v0[index] + v0[v0.size() - 1 - index]);}for (decltype(v2.size()) index = 0; index < v2.size(); index++){cout << v2[index] << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
3.21 请使用迭代器重做3.3.3节的第一个练习。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::vector;
using std::string;int main()
{vector<int> v1;cout << v1.size() << endl;for (auto it = v1.begin(); it != v1.end(); ++it){cout << *it << ",";}cout << endl;vector<int> v2(10);cout << v2.size() << endl;for (auto it = v2.begin(); it != v2.end(); ++it){cout << *it << ",";}cout << endl;vector<int> v3(10, 42);cout << v3.size() << endl;for (auto it = v3.begin(); it != v3.end(); ++it){cout << *it << ",";}cout << endl;vector<int> v4{ 10 };cout << v4.size() << endl;for (auto it = v4.begin(); it != v4.end(); ++it){cout << *it << ",";}cout << endl;vector<int> v5{ 10, 42 };cout << v5.size() << endl;for (auto it = v5.begin(); it != v5.end(); ++it){cout << *it << ",";}cout << endl;vector<string> v6{ 10 };cout << v6.size() << endl;for (auto it = v6.begin(); it != v6.end(); ++it){cout << *it << ",";}cout << endl;vector<string> v7{ 10,"hi" };cout << v7.size() << endl;for (auto it = v7.begin(); it != v7.end(); ++it){cout << *it << ",";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
3.22 修改之前那个输出text第一段的程序,首先把text的第一段全部改成大写形式,然后输出它。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::vector;
using std::string;int main()
{vector<string> v1{ "aa","bb","cc" };for (auto it = v1.begin(); it != v1.end() && !it->empty(); it++){for(auto &c:*it){ c = toupper(c);}}for (auto it = v1.begin(); it != v1.end() && !it->empty(); it++){cout << *it << ",";}cout << endl;return 0;
}![]()
3.23 编写一段程序,创建一个含有10个整数的vector对象,然后使用迭代器将所有元素的值都变成原来的两倍。输出vector对象的内容,检验程序是否正确。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::vector;
using std::string;int main()
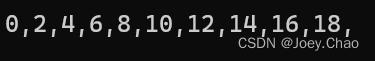
{vector<int> v1{ 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };for (auto it = v1.begin(); it != v1.end(); it++){*it = *it * 2;}for (auto it = v1.begin(); it != v1.end(); it++){cout << *it << ",";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
3.24 请使用迭代器重做3.3.3节的最后一个练习。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::vector;
using std::string;int main()
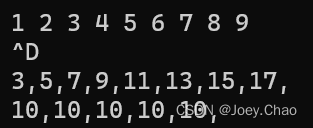
{vector<int> v0, v1, v2;int i;while (cin >> i){v0.push_back(i);}for (auto it = v0.begin(); it != v0.end() - 1; it++){v1.push_back(*it + *(it + 1));}for (auto ic : v1){cout << ic << ",";}cout << endl;if (v0.size() % 2 == 0){for (auto it = v0.begin(); it != v0.begin() + v0.size() / 2; it++){v2.push_back(*it + *(v0.end() - (it - v0.begin()) - 1));}}else{for (auto it = v0.begin(); it != v0.begin() + v0.size() / 2 + 1; it++){v2.push_back(*it + *(v0.end() - (it - v0.begin()) - 1));}}for (auto ic : v2){cout << ic << ",";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
3.25 3.3.3节划分分数段的程序是使用下标运算符实现的,请利用迭代器改写该程序实现完全相同的功能。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::vector;
using std::string;int main()
{vector<unsigned> sorces(11, 0);unsigned grade;auto it = sorces.begin();while (cin >> grade){(*(it + grade / 10))++;}for (auto it = sorces.begin(); it != sorces.end(); it++){cout << *it << ",";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
3.31 编写一段程序,定义一个含有10个int的数组,令每个元素的值就是其下标值。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::vector;
using std::string;int main()
{int va[10];for (size_t index = 0; index < 10; index++){va[index] = index;}for (auto i : va){cout << va[i] << ",";}cout << endl;return 0;
}![]()
3.32 将上一题刚刚创建的数组拷贝给另一数组。利用vector重写程序,实现类似的功能。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::vector;
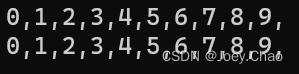
using std::string;int main()
{//数组int va[10],va1[10];for (size_t index = 0; index < 10; index++){va[index] = index;}for (size_t index = 0; index < 10; index++){va1[index] = va[index];}for (auto i : va1){cout << va1[i] << ",";}cout << endl;//vectorvector<int> ve;for (decltype(ve.size()) index = 0; index < 10; index++){ve.push_back(index);}vector<int> ve2(ve);for (auto i : ve2){cout << i << ",";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
3.34 假定p1 和 p2 都指向同一个数组中的元素,则下面程序的功能是什么?什么情况下该程序是非法的?
p1 += p2 - p1;
将p1移动(p2-p1)个位置;p1或p2是非法的,该程序就是非法的。
3.35 编写一段程序,利用指针将数组中的元素置为0。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::vector;
using std::string;int main()
{//数组int va[10],va1[10];for (size_t index = 0; index < 10; index++){va[index] = index;}for (auto i : va){cout << i << ",";}cout << endl;int* p = va;for (size_t index = 0; index < 10; index++ , p++){*p = 0;}for (auto i : va){cout << i << ",";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
3.36 编写一段程序,比较两个数组是否相等。再写一段程序,比较两个vector对象是否相等。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
bool compareva(int* const vb1,int* const ve1,int* const vb2,int* const ve2)
{if ((ve1 - vb1) == (ve2 - ve1)){return false;}else{for (int* i1 = vb1, *i2 = vb2; i1 != ve1 && i2 != ve2; i1++, i2++){if (*i1 != *i2){return false;}}}return true;
}
int main()
{//数组int v1[6] = { 0,23,66 }, v2[2];if (compareva(v1, end(v1), v2, end(v2))){cout << "equal!" << endl;}else{cout << "No equal!" << endl;}//vectorvector<int> m1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 }, m2 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 };if (m1 == m2){cout << "equal!" << endl;}else{cout << "No equal!" << endl;}return 0;
}
3.39 编写一段程序,比较两个string对象。再编写一段程序,比较两个C风格字符串的内容。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>#include <iterator>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1 = "aabbcc", s2 = "aabbcc";if (s1 == s2){cout << "Equal!" << endl;}else{cout << "No equal!" << endl;}char v1[] = { 'a','b','c' }, v2[] = "abc";if (strcmp(v1, v2)){cout << "Equal!" << endl;}else{cout << "No equal!" << endl;}return 0;
}
3.40 编写一段程序,定义两个字符数组并用字符串字面值初始化它们;接着再定义一个字符数组存放前面两个数组连接后的结果。使用strcpy和strcat把前两个数组的内容拷贝到第三个数组当中。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>const char cstr1[] = "Hello";
const char cstr2[] = "world!";int main()
{char cstr3[100];strcpy(cstr3, cstr1);strcat(cstr3, " ");strcat(cstr3, cstr2);std::cout << cstr3 << std::endl;
}
Hello world!3.41 编写一段程序,用整型数组初始化一个vector对象。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>#include <iterator>
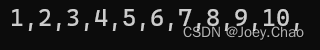
using namespace std;int main()
{int v1[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};vector<int> x1(begin(v1), end(v1));for (auto i : x1){cout << i << ",";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
3.42 编写一段程序,将含有整数元素的vector对象拷贝给一个整型数组。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>#include <iterator>
using namespace std;int main()
{vector<int> v1 = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};int v2[10];for (int index = 0; index < v1.size(); index++){v2[index] = v1[index];}for (auto i : v2){cout << i << ",";}cout << endl;return 0;
}![]()
3.43 编写3个不同版本的程序,令其均能输出ia的元素。版本1使用范围for语句管理迭代过程;版本2和版本3都使用普通for语句,其中版本2要求使用下标运算符,版本3要求使用指针。此外,在所有3个版本的程序中都要直接写出数据类型,而不能使用类型别名、auto关键字和decltype关键字。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>#include <iterator>
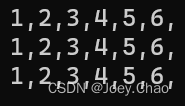
using namespace std;int main()
{int v1[2][3] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 };//1for (int (&i)[3] : v1){for (int j : i){cout << j << ",";}}cout << endl;//2for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++){for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++){cout << v1[i][j] << ",";}}cout << endl;//3for (int(*p)[3] = v1; p != v1 + 2; p++){for (int* q = *p; q != *p + 3; q++){cout << *q << ",";}}cout << endl;return 0;
}
3.44 改写上一个练习中的程序,使用类型别名来代替循环控制变量的类型。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>#include <iterator>
using namespace std;int main()
{using int_row = int[3];int v1[2][3] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 };//1for (int_row &i : v1){for (int j : i){cout << j << ",";}}cout << endl;//2for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++){for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++){cout << v1[i][j] << ",";}}cout << endl;//3for (int_row *p = v1; p != v1 + 2; p++){for (int* q = *p; q != *p + 3; q++){cout << *q << ",";}}cout << endl;return 0;
}
3.45 再一次改写程序,这次使用auto关键字。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>#include <iterator>
using namespace std;int main()
{int v1[2][3] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 };//1for (auto &i : v1){for (auto j : i){cout << j << ",";}}cout << endl;//2for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++){for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++){cout << v1[i][j] << ",";}}cout << endl;//3for (auto *p = v1; p != v1 + 2; p++){for (int* q = *p; q != *p + 3; q++){cout << *q << ",";}}cout << endl;return 0;
}