0. 省流
{"version": "0.2.0","configurations": [{"name": "调试train.py文件","type": "debugpy","request": "launch","program": "train.py","console": "integratedTerminal","python": "/home/leovin/anaconda3/envs/wsl/bin/python","args": ["--weights","weights/yolov5s.pt","--cfg","models/yolov5s.yaml"]}]
}
其中:
"name":debug配置的名称(任意)"program":要debug的文件("${file}"为当前打开的文件)"python":使用的虚拟环境的 Python 路径;"args":"args": ["参数1", "参数2", ...]:传入固定参数"args: "${command:pickArgs}":运行后再填写参数,没有则直接回车
1. 问题
在使用 VSCode 进行 Debug 时,如果程序没有额外的参数要求,那我们直接在右上角点击 Debug 即可开始调试。
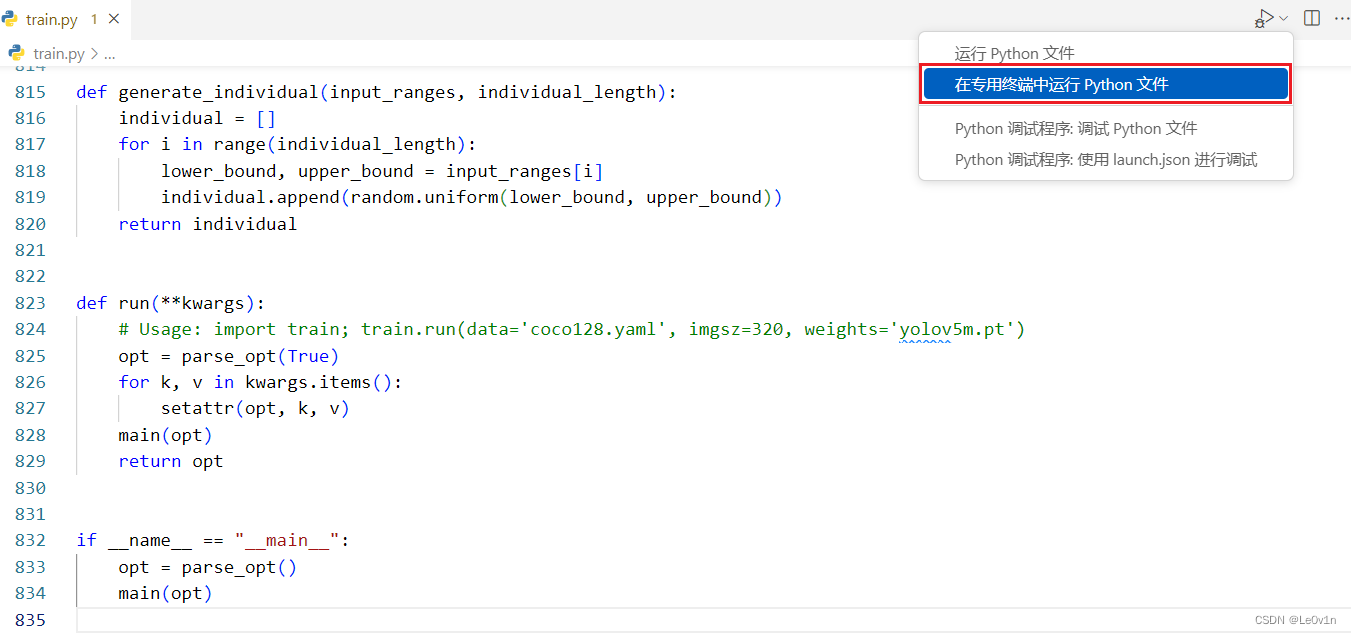
但如果我们的程序需要传入指定的参数才能正常运行,那么直接点击右上角的 Debug 按钮是不行的。
以 YOLOv5 为例,我们想要在 Debug 的时候传入一些参数,如:
python train.py \--weights weights/yolov5s.pt \--cfg models/yolov5s.yaml \--data data/coco.yaml\--img 640 \--device 0 \--project runs/train \--name exp
2. 使用 lanuch.json 进行调试
2.1 launch.json 文件的创建
如果我们直接点击右上角的 debug 按钮,程序使用的是默认的配置,这与我们的需求不合。我们可以使用 “Python调试程序:使用 launch.json 进行调试”,如下图所示:

之后点击“添加配置”,此时 VSCode 会自动创建一个 launch.json 文件:
{// 使用 IntelliSense 了解相关属性。 // 悬停以查看现有属性的描述。// 欲了解更多信息,请访问: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387"version": "0.2.0","configurations": [{"name": "Python 调试程序: 包含参数的当前文件","type": "debugpy","request": "launch","program": "${file}","console": "integratedTerminal","args": "${command:pickArgs}"}]
}
2.2 launch.json 关键字说明
| 关键字 | 作用 |
|---|---|
// | Json 文件的注释 (可以删除) |
"version" | 调试配置文件的版本 |
"configurations" | 包含了所有的调试配置的数组 |
"name" | 调试配置的名称 在 VSCode 的调试侧边栏中显示,区分不同的调试配置 |
"type" | 调试器的类型 (通常是 "python" 或者 "debugpy") |
"request" | 启动模式 ( "launch" 用于启动一个新的程序,而 "attach" 用于附加到已经运行的程序) |
"program" | 要调试的程序的路径 |
"args" | 传递给程序的命令行参数的数组 |
2.2.1 “names” 关键字说明
"name" 关键字并不是要调试的文件的名称,而是调试配置的名称,所以我们可以任意写:
{"version": "0.2.0","configurations": [{"name": "调试当前文件","type": "debugpy","request": "launch","program": "${file}","console": "integratedTerminal","args": "${command:pickArgs}"},{"name": "调试train.py文件","type": "debugpy","request": "launch","program": "train.py","console": "integratedTerminal","args": ["--weights","weights/yolov5s.pt","--cfg","models/yolov5s.yaml"]}]
}
上面我们就有了两个不同的配置,侧栏中可以任意切换:
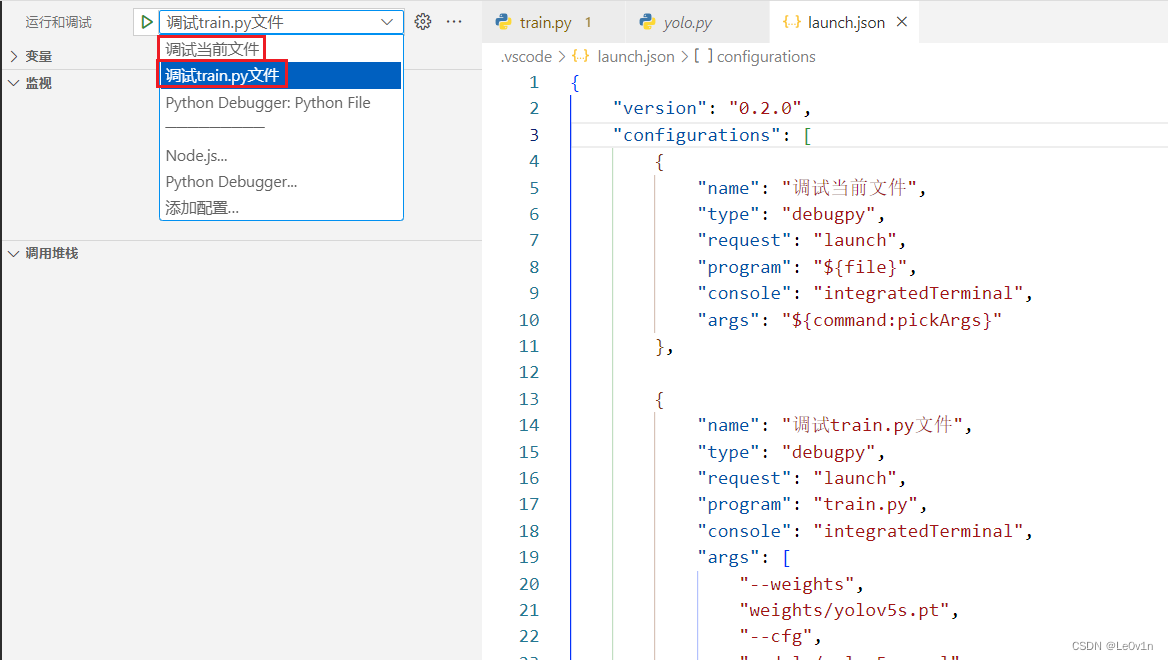
2.2.2 “program” 关键字说明
"program" 关键字才是要调试的文件的名称,默认为 "${file}",表示 VSCode 编辑器当前打开的文件
2.2.3 “args” 关键字说明
"args" 关键字是我们想要传入的参数,默认是 "${command:pickArgs}",它允许用户在启动调试会话之前通过一个命令界面来选择或输入命令行参数,比如:
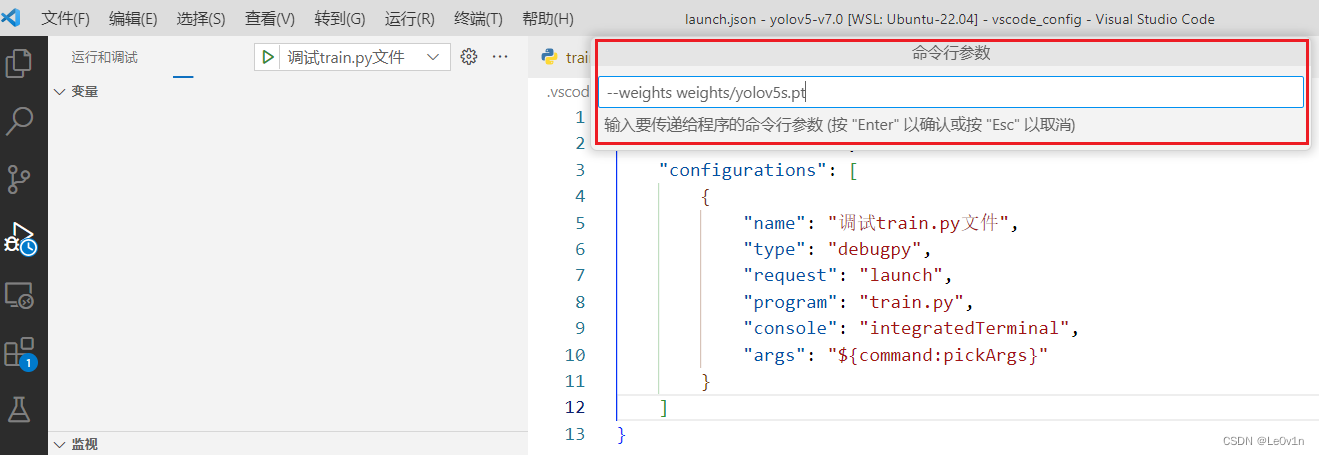
我们也可以直接用数组写入我们要传入的参数:
{"version": "0.2.0","configurations": [{"name": "调试train.py文件","type": "debugpy","request": "launch","program": "train.py","console": "integratedTerminal","args": ["--weights","weights/yolov5s.pt","--cfg","models/yolov5s.yaml"]}]
}
2.3 示例
利用这些关键字,我们可以自定义如何调试程序,比如我们想要传入参数即可按下面进行:
{"version": "0.2.0","configurations": [{"name": "调试train.py文件","type": "debugpy","request": "launch","program": "${file}","console": "integratedTerminal","args": ["--weights","weights/yolov5s.pt","--cfg","models/yolov5s.yaml"]}]
}
我们直接在侧栏进行调试:
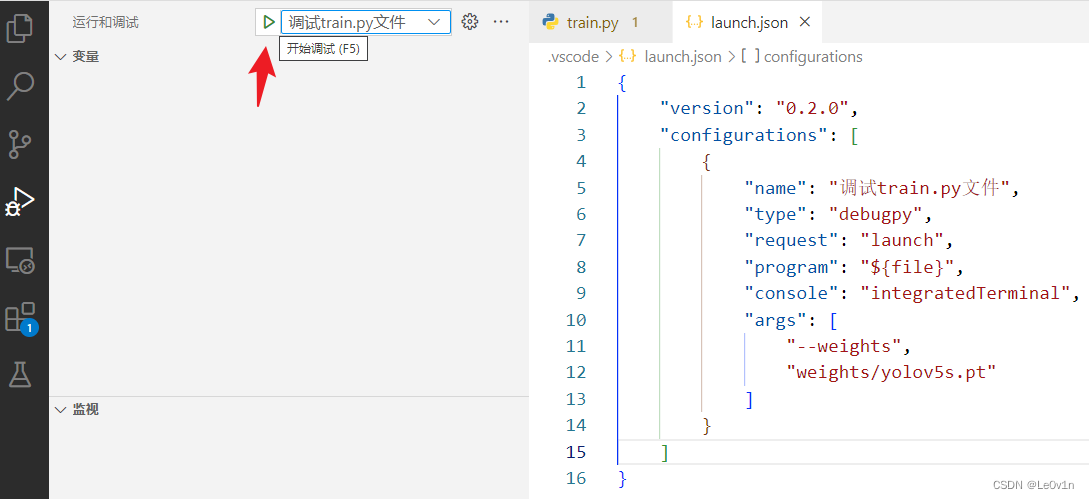

我们发现程序虽然带有 --weights weights/yolov5s.pt --cfg models/yolov5s.yaml,但 debug 程序直接后就停止了,这是为什么?
这是因为我们的 lanuch.json 文件中的 "program" 关键字是 "${file}",即debug程序会对当前文件进行debug,但我们当前的文件是 launch.json 文件,所以程序就停止了 😂。
那么为了让其可以正常调试我们的 train.py 文件,我们选择该文件后再启用debug:
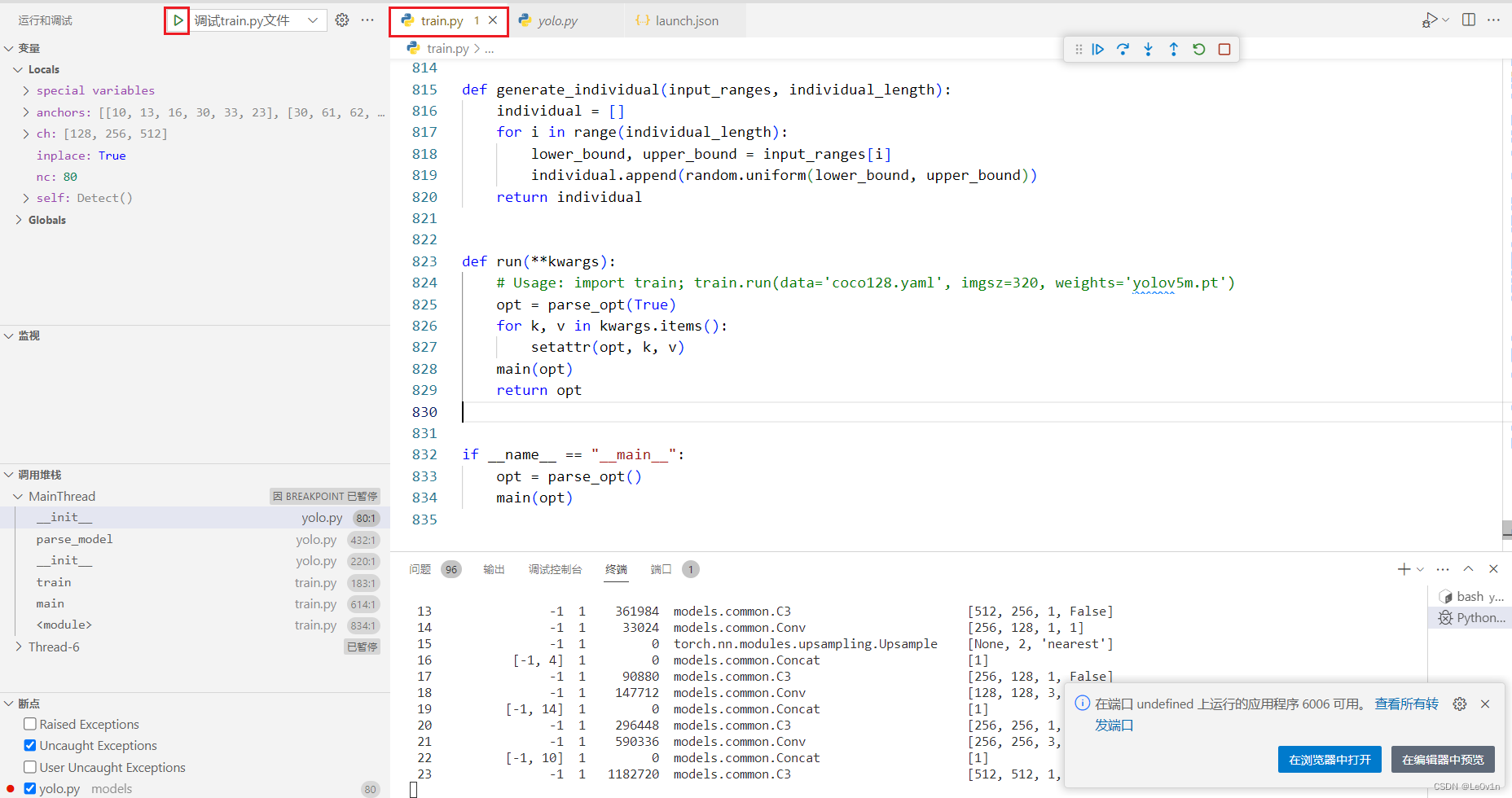
此时我们发现我们的debug正常开启了。
其实我们还有一个方法,那就是让 "program" 关键字写死:
{"version": "0.2.0","configurations": [{"name": "调试train.py文件","type": "debugpy","request": "launch","program": "train.py","console": "integratedTerminal","args": ["--weights","weights/yolov5s.pt","--cfg","models/yolov5s.yaml"]}]
}
这样无论我们打开哪个文件,直接在侧栏debug都是对 train.py 文件进行debug:
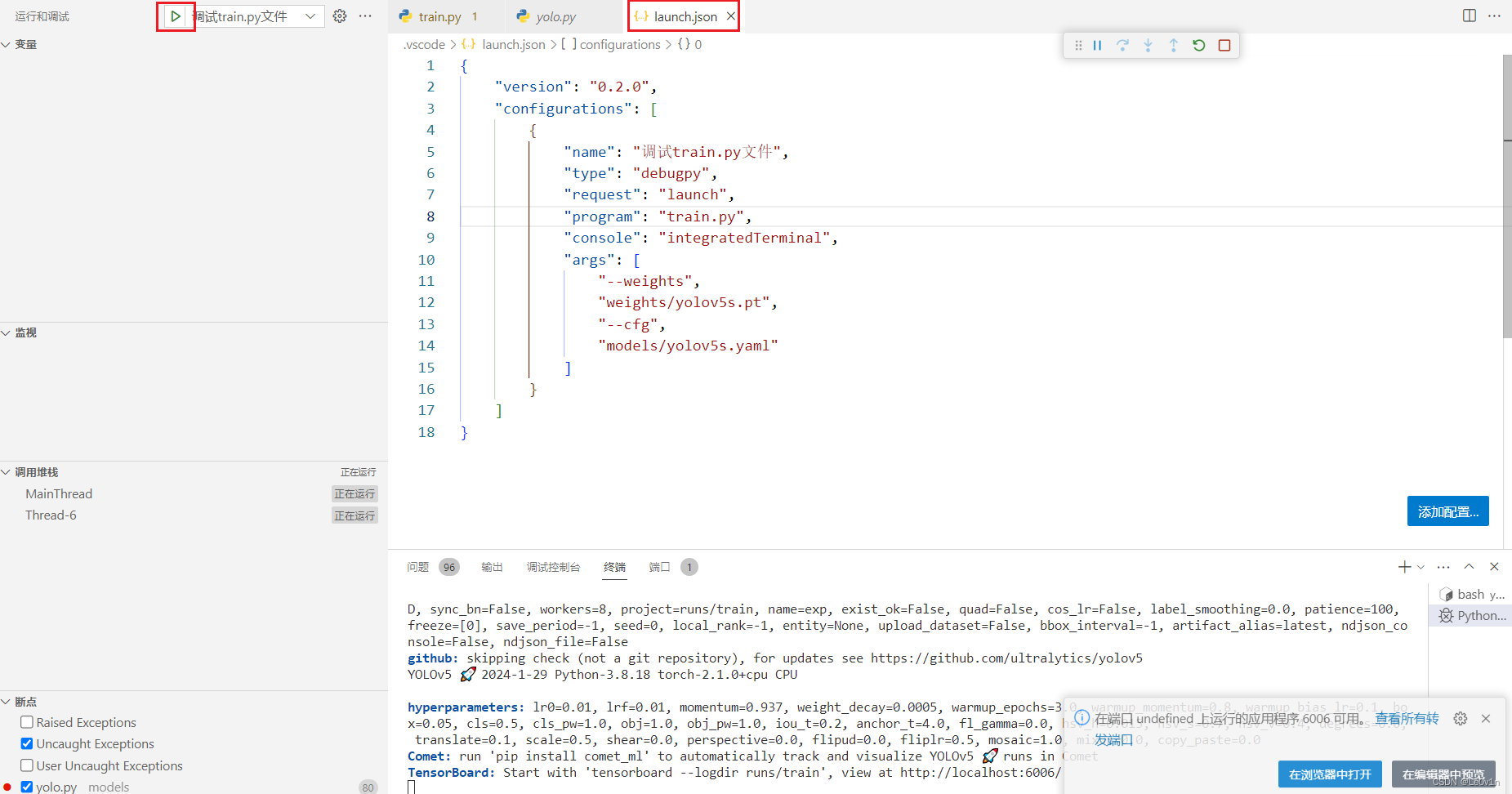
2.4 如何在 debug 前进入指定虚拟环境
2.4.1 〔⭐方法1〕利用 “python” 关键字
我们可以使用 "python" 关键字直接指定使用的 Python 路径:
{"version": "0.2.0","configurations": [{"name": "调试train.py文件","type": "debugpy","request": "launch","program": "train.py","console": "integratedTerminal","python": "/home/leovin/anaconda3/envs/wsl/bin/python","args": ["--weights","weights/yolov5s.pt","--cfg","models/yolov5s.yaml"]}]
}
💡 Tips:我们可以使用下面的命令查看 Python 的路径:
conda activate env_name # 先激活我们的虚拟环境which python # 在 macOS 或 Linux 上
where python # 在 Windows 上
2.4.2 〔方法2〕在运行终端手动切换环境
首先我们先运行一遍 launch.json 的 debug,之后我们停止(打断),在之后我们手动激活虚拟环境:
conda activate env_name
最后我们再运行 launch.json 的 debug。