基本介绍
Feign是一种负载均衡的HTTP客户端, 使用Feign调用API就像调用本地方法一样,从避免了调用目标微服务时,需要不断的解析/封装json 数据的繁琐。Feign集成了Ribbon。Ribbon+eureka是面向微服务编程,而Feign是面向接口编程。
Fegin是一个声明似的web服务客户端,它使得编写web服务客户端变得更加容易。使用Fegin创建一个接口并对它进行注解。它具有可插拔的注解支持包括Feign注解与JAX-RS注解,Feign还支持可插拔的编码器与解码器,Spring Cloud 增加了对 Spring MVC的注解,Spring Web 默认使用了HttpMessageConverters, Spring Cloud 集成 Ribbon 和 Eureka 提供的负载均衡的HTTP客户端 Feign。
Feign能干什么
Feign旨在使编写Java Http客户端变得更容易。在使用Ribbon+RestTemplate时,利用RestTemplate对http请求的封装处理,形成了一套模版化的调用方法。但是在实际开发中,由于对服务依赖的调用可能不止一处,往往一个接口会被多处调用,所以通常都会针对每个微服务自行封装一些客户端类来包装这些依赖服务的调用。所以,Feign在此基础上做了进一步封装,由他来帮助我们定义和实现依赖服务接口的定义。在Feign的实现下,我们只需创建一个接口并使用注解的方式来配置它(以前是Dao接口上面标注Mapper注解,现在是一个微服务接口上面标注一个Feign注解即可),即可完成对服务提供方的接口绑定,简化了使用Spring cloud Ribbon时,自动封装服务调用客户端的开发量。
Feign集成了Ribbon。利用Ribbon维护了MicroServiceCloud-Dept的服务列表信息,并且通过轮询实现了客户端的负载均衡。而与Ribbon不同的是,通过feign只需要定义服务绑定接口且以声明式的方法,优雅而简单的实现了服务调用。
SpringCloud之Feign入门实例
1、添加依赖以及主程序
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-feign</artifactId></dependency>@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@EnableFeignClients(basePackages= {"com.atguigu.springcloud"})
@ComponentScan("com.atguigu.springcloud")
public class DeptConsumer80_Feign_App{public static void main(String[] args){SpringApplication.run(DeptConsumer80_Feign_App.class, args);}
}2、接口+注解(一般在公共接口中定义,方面其他微服务调用)
@FeignClient(value = "MICROSERVICECLOUD-DEPT") //该接口对应于应用id为MICROSERVICECLOUD-DEPT的微服务
public interface DeptClientService
{@RequestMapping(value = "/dept/get/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)public Dept get(@PathVariable("id") long id);@RequestMapping(value = "/dept/list",method = RequestMethod.GET)public List<Dept> list();@RequestMapping(value = "/dept/add",method = RequestMethod.POST)public boolean add(Dept dept);
}应用id为MICROSERVICECLOUD-DEPT的微服务就实现该接口功能。
3、Web层服务调用
以前使用Ribbon+Eureka时:
@RestController
public class DeptController_Consumer{private static final String REST_URL_PREFIX = "http://MICROSERVICECLOUD-DEPT";@Autowiredprivate RestTemplate restTemplate;@RequestMapping(value = "/consumer/dept/add")public boolean add(Dept dept){return restTemplate.postForObject(REST_URL_PREFIX + "/dept/add", dept, Boolean.class);}@RequestMapping(value = "/consumer/dept/get/{id}")public Dept get(@PathVariable("id") Long id){return restTemplate.getForObject(REST_URL_PREFIX + "/dept/get/" + id, Dept.class);}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")@RequestMapping(value = "/consumer/dept/list")public List<Dept> list(){return restTemplate.getForObject(REST_URL_PREFIX + "/dept/list", List.class);}
}
现在使用Feign,面向接口编程:
@RestController
public class DeptController_Consumer{@Autowiredprivate DeptClientService service;@RequestMapping(value = "/consumer/dept/get/{id}")public Dept get(@PathVariable("id") Long id){return this.service.get(id);}@RequestMapping(value = "/consumer/dept/list")public List<Dept> list(){return this.service.list();}@RequestMapping(value = "/consumer/dept/add")public Object add(Dept dept){return this.service.add(dept);}
}Ribbon和Feign都是用于调用其他服务的,不过方式不同
目前,在Spring cloud 中服务之间通过restful方式调用有两种方式
- restTemplate+Ribbon
- feign
- 1.启动类使用的注解不同,Ribbon用的是@RibbonClient,Feign用的是@EnableFeignClients。
- 2.服务的指定位置不同,Ribbon是在@RibbonClient注解上声明,Feign则是在定义抽象方法的接口中使用@FeignClient声明。
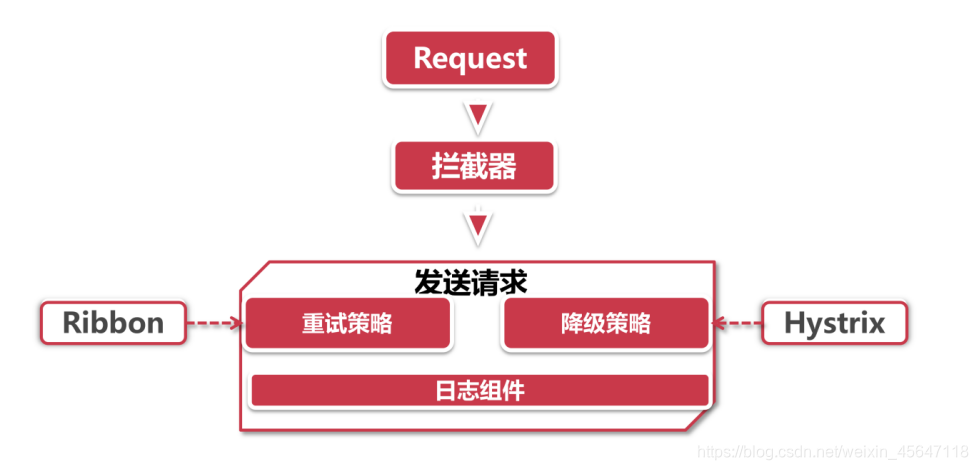
- 3.调用方式不同,Ribbon需要自己构建http请求,模拟http请求然后使用RestTemplate发送给其他服务,步骤相当繁琐。Feign则是在Ribbon的基础上进行了一次改进,采用接口的方式,将需要调用的其他服务的方法定义成抽象方法即可,不需要自己构建http请求。不过要注意的是抽象方法的注解、方法签名要和提供服务的方法完全一致。
Feign的自带断路器
@FeignClient(value = "YunCai-SearchServer", fallback=ServiceHystrix.class)
public interface SchedualServiceHi {@RequestMapping(value = "/luke/itemsearch",method = RequestMethod.GET)ResponseMap sayHiFromClientOne(@RequestParam(value = "start") Integer start,@RequestParam(value = "rows") Integer rows,@RequestParam(value = "tenantId") Integer tenantId,@RequestParam(value = "status") Integer status,@RequestParam(value = "key") String key);
}@Component
public class ServiceHystrix implements SchedualServiceHi {@Overridepublic ResponseMap sayHiFromClientOne(Integer start, Integer rows, Integer tenantId, Integer status, String key) {SearchResult result = new SearchResult(0, new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1L,2L,3L)));return new ResponseMap(false, "111", 506, result);}
}