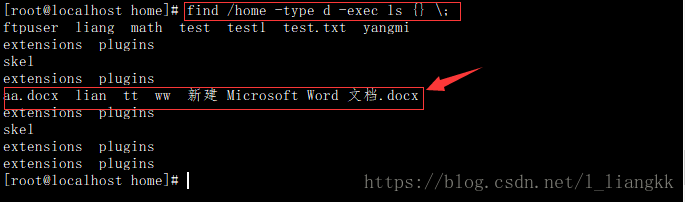
基础打印操作
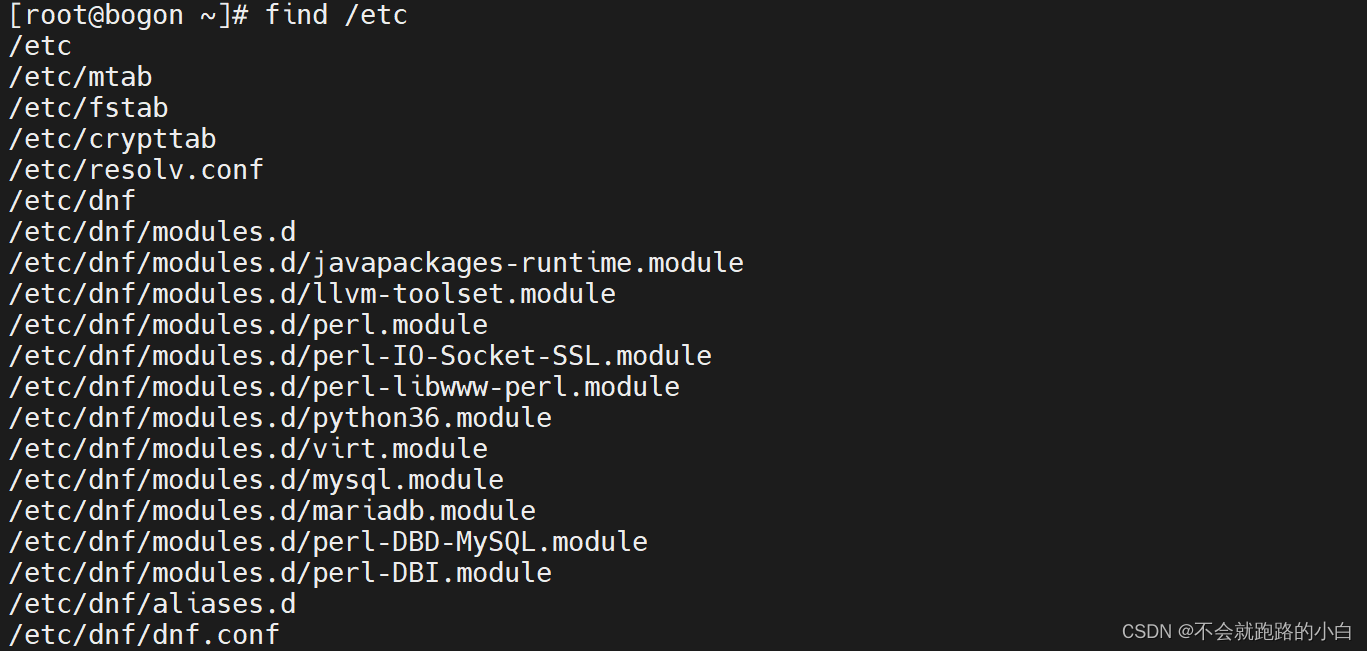
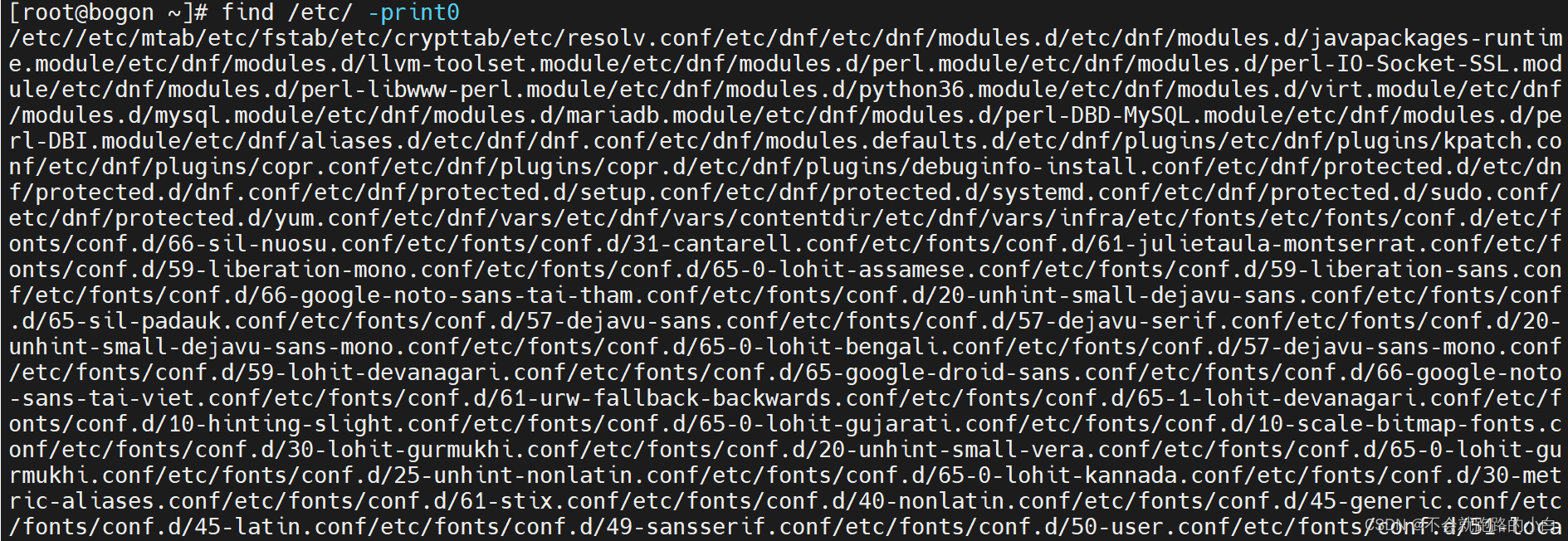
find命令默认接的命令是-print,它默认以\n将找到的文件分隔。可以使用-print0来使用\0分隔,这样就不会分行了。但是一定要注意,-print0针对的是\n转\0,如果查找的文件名本身就含有空格,则find后-print0仍然会显示空格文件。所以-print0实现的是\n转\0的标记,可以使用其他工具将\0标记替换掉,如xargs,tr等。
注意:如果find命令后没有加命令,那么find查找当前所在的目录进行查找。
文件名搜索
常用的两个是-name和-path。
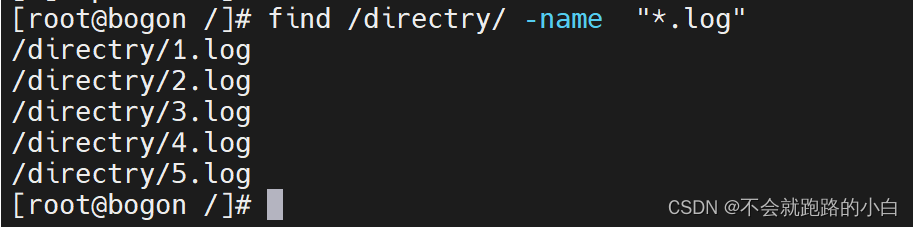
-name可以对文件的basename进行匹配,
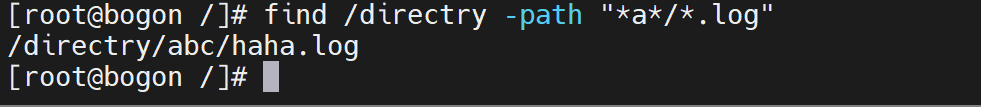
-path可以对文件的dirname+basename。查找的文件名最好使用引号包围,可以配合通配符进行查找。
注意:但不能在-name的模式中使用”/“,除非文件名中包含了字符”/“,否则将匹配不到任何东西,因为-name只对basename进行匹配。例如,想要匹配/tmp目录下某包含字符a的目录下的log文件。
注意,配合通配符[]时应该注意是基于字符顺序的,大小写字母的顺序是a-z –> A-Z,指定[a-z]表示小写字母a-z,同理[A-Z],而[a-zA-Z]和[a-Z]都表示所有大小写字母。当然还可以指定[a-A]表示a-z外加一个A。
字母的处理顺序较容易理解,关于数字的处理方法,见下面的示例。
[root@bogon directry]# find -name "[1-4].log"
./1.log
./2.log
./3.log
./4.log
[root@bogon directry]# find -name "[1-20].log"
./1.log
./2.log
./0.log
[root@bogon directry]# find -name "[1-23].log"
./1.log
./2.log
./3.log
[root@bogon directry]# find -name "[1-22-3].log"
./1.log
./2.log
./3.log
从上面结果可以看出,其实[]只能匹配单个字符,[0-9]表示0-9的数字,[1-20]表示[1-2]外加一个0,[1-23]表示[1-2]外加一个3,[1-22-3]表示[1-2]或[2-3],迷惑点就是看上去是大于10的整数,其实是两个或者更多的单个数字组合体。也可以用这种方法表示多种匹配:[1-2,2-3]。
根据文件类型搜索 -type
一般需要搜索的文件类型就只有普通文件(f),目录(d),链接文件(l)。
[root@bogon directry]# find -type f -name '*.log'
./1.log
./2.log
./3.log
./4.log
./5.log
./abc/haha.log
./0.log
[root@bogon directry]# find -type d -name 'a*'
./abc
根据文件时间戳搜索
最基础的时间戳包括:
-atime:显示的是文件中的数据最后被访问的时间,比如系统的进程直接使用或通过一些命令和脚本间接使用。(执行一些可执行文件或脚本)。
-mtime:显示的是文件内容被修改的最后时间,比如用vi编辑时就会被改变。(也就是Block的内容)
-ctime:显示的是文件的权限、拥有者、所属的组、链接数发生改变时的时间。当然当内容改变时也会随之改变(即inode内容发生改变和Block内容发生改变时)。
[root@bogon directry]# find -type f -mtime -30 -name "*.log"
./1.log
./2.log
./3.log
./4.log
./5.log
./abc/haha.log
./0.log
根据文件大小搜索
例如搜索/directry下大于0K的.log文件
[root@bogon directry]# find -type f -size +0k -name '*.log'
./1.log
./0.log
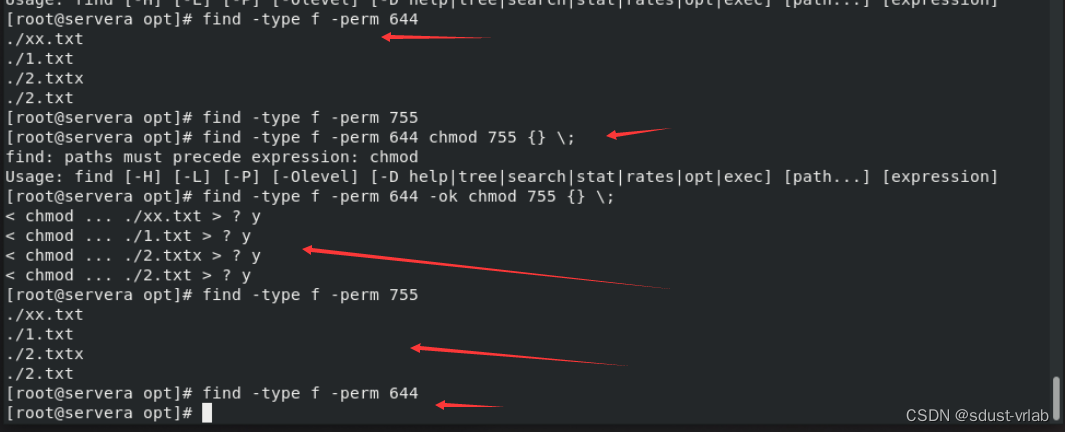
根据权限搜索:-perm
[root@bogon directry]# find -type f -perm 0644 -name '*.log'
./2.log
./3.log
./4.log
./5.log
./abc/haha.log
./1.log
./0.log
[root@bogon directry]# ll
total 8
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 992 Jan 14 06:31 0.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 Jan 14 06:26 1.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 14 06:00 2.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 14 06:00 3.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 14 06:00 4.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 14 06:00 5.log
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 22 Jan 14 06:05 abc
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 14 06:14 touch
搜索空文件
空文件可以是没有任何内容的普通文件,也可以是没有任何内容的目录。
例如搜索目录中没有文件的空目录 空文件。
[root@bogon directry]# find -type d -empty
./abc
[root@bogon directry]# find -type f -empty
./2.log
./3.log
./4.log
./5.log
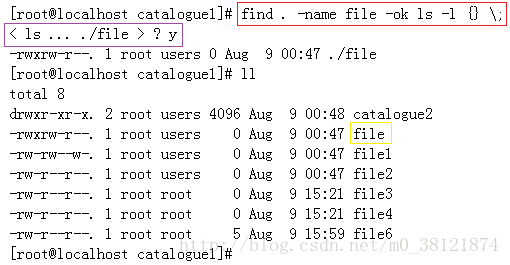
搜索到文件后并删除
例如搜索到/directry下的”.log”文件然后删除。
[root@bogon directry]# ll
total 8
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 992 Jan 14 06:31 0.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 Jan 14 06:26 1.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 14 06:00 2.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 14 06:00 3.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 14 06:00 4.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 14 06:00 5.log
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 22 Jan 14 06:05 abc
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 14 06:14 touch
[root@bogon directry]# find -type f -name "*.log" -exec rm -rf '{}' \;
[root@bogon directry]# ll
total 0
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Jan 14 06:39 abc
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jan 14 06:14 touch
搜索指定日期范围的文件
例如搜索/test下2021-06-03到2021-06-06之间修改过的文件。
$ find /test -type f -newermt 2021-06-03 -a ! -newermt 2021-06-06
或者,创建两个临时文件,并用touch修改这两个文件的修改时间,然后find -newer去参照这两个文件。
$ touch -m -d 2017-06-03 tmp1.txt
$ touch -m -d 2017-06-06 tmp2.txt
$ find /test -type f -newer tmp1.txt -a ! -newer tmp2.txt
并行加速搜索
有时候,想要搜索的内容并不知道在哪里,这时我们会从根”/“开始搜索,这样的搜索速度可能会稍微长那么一点点。为了加速搜索,使用xargs的并行功能。例如,搜索”/“下的所有”.log”结尾的文件:
[root@bogon directry]# ls --hide proc / | xargs -i -P 0 find /{} -type f -name "*.log" /1.log
/2.log
/3.log
/4.log
/5.log
/home/sun/.local/share/gvfs-metadata/home-65477e94.log
/var/lib/mysql/tc.log
/var/log/audit/audit.log
/var/log/sssd/sssd.log
/var/log/sssd/sssd_implicit_files.log
/var/log/sssd/sssd_nss.log
/var/log/sssd/sssd_kcm.log
/var/log/tuned/tuned.log
/var/log/anaconda/anaconda.log
/var/log/anaconda/X.log
/var/log/anaconda/program.log
/var/log/anaconda/packaging.log
/var/log/anaconda/storage.log
/var/log/anaconda/lvm.log
/var/log/anaconda/dnf.librepo.log
/var/log/anaconda/hawkey.log
/var/log/anaconda/dbus.log
/var/log/anaconda/ks-script-2eqowa86.log
/var/log/anaconda/ks-script-883u3o8h.log
/var/log/anaconda/ks-script-qijn4v0c.log
/var/log/anaconda/ks-script-w2hkk999.log
/var/log/anaconda/journal.log
/var/log/boot.log
/var/log/vmware-vmtoolsd-root.log
/var/log/vmware-vmsvc-root.log
/var/log/vmware/rc.local.log
/var/log/kdump.log
/var/log/dnf.log
/var/log/dnf.librepo.log
/var/log/dnf.rpm.log
/var/log/hawkey.log
/var/log/mariadb/mariadb.log
/var/log/vmware-network.3.log
/var/log/vmware-network.2.log
/var/log/vmware-network.1.log
/var/log/vmware-network.log
/usr/lib/rpm/rpm.log
获取文件绝对路径
当find结合管道,而管道后的命令很可能想要获取到搜索到的文件的绝对路径,或者说是全路径。而问题是,当find的搜索路径是相对路径时,搜索出来的显示结果也是以相对路径显示的。
三种形式参考
[root@bogon directry]# find '*.log' $(pwd)
find: ‘*.log’: No such file or directory
/directry
/directry/abc
/directry/touch
/directry/1.log
/directry/2.log
/directry/3.log
/directry/4.log
/directry/5.log
[root@bogon directry]# find '*.log' $PWD
find: ‘*.log’: No such file or directory
/directry
/directry/abc
/directry/touch
/directry/1.log
/directry/2.log
/directry/3.log
/directry/4.log
/directry/5.log
[root@bogon directry]# find '*.log' ~+
find: ‘*.log’: No such file or directory
/directry
/directry/abc
/directry/touch
/directry/1.log
/directry/2.log
/directry/3.log
/directry/4.log
/directry/5.log
获取文件名部分(basename)
find的-printf选项有很多修饰符功能,对于处理路径方面的修饰符有%f、%p、%P,其中%f是获取basename(去除所有路径前缀),%p是获取路径自身,一般用不上,%P是获取除了find搜索路径的剩余部分。
首先,想要获取basename,建议使用%f
[root@bogon /]# find /directry/ -printf "%f\n"
directry/
abc
touch
1.log
2.log
3.log
4.log
5.log[root@bogon /]# find /directry/ -printf "%p\n"
/directry/
/directry/abc
/directry/touch
/directry/1.log
/directry/2.log
/directry/3.log
/directry/4.log
/directry/5.log再看使用%P的效果。结果仅仅是去掉了find搜索路径/tmp/test部分。当搜索路径只有一层(即没有子目录)时,它也可以用来获取basename。
[root@bogon /]# find /directry/ -printf "%P\n"
abc
touch
1.log
2.log
3.log
4.log
5.log
从结果中排除目录自身
find搜索目录时,总是会将搜索路径自身也包含到搜索结果中。想办法排除它是必须的。
排除的方法是,加上一个-path选项并取反,-path的参数和find的搜索路径参数必须一致。
[root@bogon /]# find /directry/ ! -path /directry/
/directry/abc
/directry/touch
/directry/1.log
/directry/2.log
/directry/3.log
/directry/4.log
/directry/5.log
[root@bogon /]# find /directry/
/directry/
/directry/abc
/directry/touch
/directry/1.log
/directry/2.log
/directry/3.log
/directry/4.log
/directry/5.log