1.先检查有没有安装mariadb,有的话将其卸载,不然会和mysql冲突
[root@web1 ~]# yum list | grep mariadb2.卸载mariadb,按Y确认
[root@web1 ~]# yum remove mariadb-libs.x86_64 3.下载mysql
[root@web1 ~]# wget https://downloads.mysql.com/archives/get/p/23/file/mysql-8.0.26-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.xz
4.解压mysql
[root@web1 ~]# tar -xvf mysql-8.0.26-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.xz 5.将压缩包移动到usr/local目录下,并重命名文件为mysql
[root@web1 ~]# mv mysql-8.0.26-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64 /usr/local/mysql
6.创建数据存放目录
[root@web1 ~]# cd /usr/local/mysql/
[root@web1 mysql]# mkdir data
[root@web1 mysql]# ls
bin data docs include lib LICENSE man README share support-files
[root@web1 mysql]#
7.创建用户组和用户
[root@web1 mysql]# groupadd mysql
[root@web1 mysql]# useradd -g mysql mysql
8.修改mysql数据库权限
[root@web1 mysql]# chown -R mysql.mysql /usr/local/mysql/
9.初始化数据库
[root@web1 mysql]# ./bin/mysqld --user=mysql --basedir=/usr/local/mysql --datadir=/usr/local/mysql/data --initialize

需要注意:记录一下mysql数据库的临时密码 u4PfDmi8F-0I后面安装步骤是需要使用的,否则需要重新安装数据库或其他方式获取密码。
10.修改配置文件vim/etc/my.conf
[root@web1 ~]# vim /etc/my.conf[mysqld]basedir = /usr/local/mysqldatadir = /usr/local/mysql/datasocket = /usr/local/mysql/mysql.sockcharacter-set-server=utf8port = 3306sql_mode=NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES[client]socket = /usr/local/mysql/mysql.sockdefault-character-set=utf811.创建MySQL服务
1)将mysql.server启动文件复制到/etc/init.d目录,使用cp -a /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld命令。
2)赋予权限,使用chmod +x /etc/rc.d/init.d/mysqld命令;
3)使用chkconfig --add mysqld创建mysql服务。
[root@web1 ~]# cp -a /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld
[root@web1 ~]# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/init.d/mysqld
[root@web1 ~]# chkconfig --add mysqld
12.检查mysql服务是否生效
[root@web1 ~]# chkconfig --list mysqld注:该输出结果只显示 SysV 服务,并不包含
原生 systemd 服务。SysV 配置数据
可能被原生 systemd 配置覆盖。 要列出 systemd 服务,请执行 'systemctl list-unit-files'。查看在具体 target 启用的服务请执行'systemctl list-dependencies [target]'。mysqld 0:关 1:关 2:开 3:开 4:开 5:开 6:关
13. 配置全局环境变量
编辑/etc/profile文件,使用vim /etc/profile命令,在profile文件中添加如下两行配置
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/mysql/bin:/usr/local/mysql/lib
export PATH
设置环境变量立即生效使用source /etc/profile命令
[root@web1 ~]# source /etc/profile
14.启动mysql
[root@web1 ~]# service mysql start
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl start mysql.service
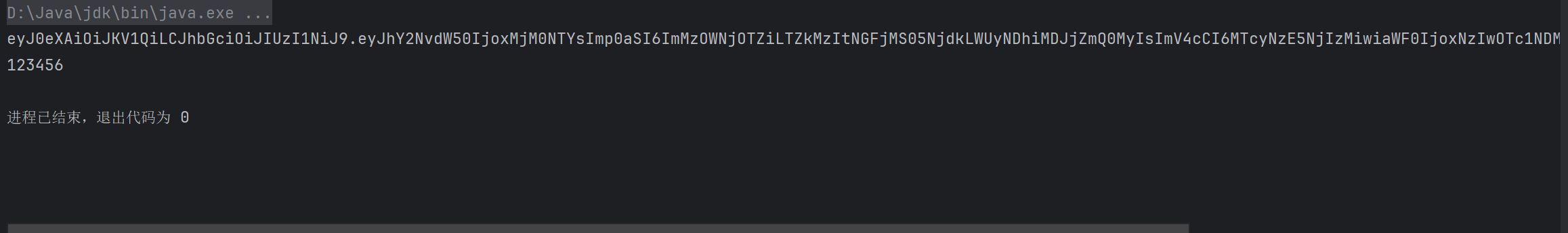
15.登录mysql,密码为初始化:u4PfDmi8F-0I
[root@web1 ~]# mysql -uroot -p
Enter password: u4PfDmi8F-0I
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 10
Server version: 8.0.26Copyright (c) 2000, 2021, Oracle and/or its affiliates.Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.mysql> 修改mysql数据库密码,使用ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY '123456';命令。
mysql> ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY '123456';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
16、设置mysql远程登录
1)切换数据库,使用use mysql;命令。
2)刷新mysql权限,使用flush privileges;命令。
mysql> use mysql;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -ADatabase changed
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
















![[MySQL][内置函数][日期函数][字符串函数][数学函数]详细讲解](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/2253db6662d84bf2a90f83d8eb13747b.png)