Title
题目
CCSI: Continual Class-Specific Impression for data-free class incremental learning
CCSI: 数据无关类别增量学习的持续类特定印象
01
文献速递介绍
当前用于医学影像分类任务的深度学习模型表现出令人鼓舞的性能。这些模型大多数需要在训练之前收集所有的训练数据并指定所有的类别。它们在部署期间训练一次深度学习模型,并期望其在所有后续数据上执行。然而,这种要求限制了在实际临床环境中的可行性,因为医学图像数据会不断收集并随着时间而变化,例如,当新疾病类型出现时。
一种解决这一挑战的有前途的方法是使系统能够进行持续或终身学习,这意味着部署的模型可以适应新数据,同时保持从以前数据中获得的信息。结合这些学习技术将使深度学习模型更灵活地适应医学数据集的不断扩展。医学持续学习已在各种增量场景中被利用(van de Ven等人,2022),考虑到新进数据的非静态特性。这些场景包括任务增量学习(González等人,2023;Liao等人,2022;Xu等人,2022;Kaustaban等人,2022;Chakraborti等人,2021),在这些场景中,引入了新的医学任务,例如,扩展一个分割网络到另一个身体区域;类别增量学习(Chee等人,2023;Yang等人,2021a;Li等人,2022),其中引入了新的疾病类别。
Abstract
摘要
在实际临床环境中,传统基于深度学习的分类方法在诊断新引入的疾病类型时会遇到困难,因为这些方法需要从所有疾病类别中获取样本进行离线训练。类别增量学习提供了一种有前途的解决方案,它通过适应已训练在特定疾病类别上的深度网络来处理新疾病。然而,灾难性遗忘问题会在适应模型到新数据时出现,导致早期类别的性能下降。之前提出的解决这一问题的方法需要永久存储以前的样本,这在医疗保健领域可能会带来隐私和存储法规方面的实际问题。为此,我们提出了一种新颖的无数据类别增量学习框架,通过对已学习类别进行数据合成,而不是存储先前类别的数据。我们的主要贡献包括获取称为“持续类特定印象”(CCSI)的合成数据,这些数据用于以前无法访问的训练类别,并提出了一种有效利用这些数据在引入新类别时更新网络的方法。我们通过对以前类别的训练分类模型的梯度进行数据反演,从每个类别的平均图像开始获取CCSI,这个过程受到医学图像中常见标志的启发,并在这个逐像素优化过程中使用持续归一化层统计作为正则化器。随后,我们通过结合合成数据和新类别数据来更新网络,并结合多种损失函数,包括一个用于在合成数据上训练的深度网络泛化到真实数据的域内对比损失、一个增加以前类别和新类别间分离的边缘损失,以及一个缓解训练数据中分布不平衡负面影响的余弦归一化交叉熵损失。大量实验表明,该框架在四个公共MedMNIST数据集和内部的心超电影系列中实现了最先进的性能,相较于基线无数据方法,分类准确率提高了高达51%。
Method
方法
This section is structured as follows. We begin by explaining theproblem setting of data-free incremental learning in Section 3.1. Next,in Section 3.2, we identify the challenges in the setting and give anoverview of our proposed pipeline, emphasizing three crucial factorsthat drive our design: (1) normalization layer, (2) data synthesis, and (3)loss functions*. Furthermore, we elaborate on the techniques suggestedto tackle the first two factors in Section 3.3. Finally, we present the newloss terms utilized to address the third factor in Section 3.4.
本节结构如下。我们首先在第3.1节解释无数据增量学习的问题设定。接下来,在第3.2节中,我们识别该设定中的挑战并概述我们提出的流程,强调驱动我们设计的三个关键因素:(1) 归一化层,(2) 数据合成,和 (3) 损失函数。此外,我们在第3.3节详细介绍了应对前两个因素的建议技术。最后,在第3.4节中,我们介绍了用于解决第三个因素的新损失项。
Conclusion
结论
In this work, we propose CCSI, a novel data-free class incrementallearning framework for medical image classification. In CCSI, we synthesize class-specific images by inverting from the trained model withclass-mean image initialization. We explore a recently introduced normalization layer – CN, to reduce overwriting moments during continualtraining and propose a novel statistic regularization using the frozenCN moments for image synthesis. Subsequently, we continue trainingon new classes and synthesized images using the proposed novel lossesto increase the utility of synthesized data by mitigating domain shiftbetween new synthesized and original images of old classes and alleviating catastrophic forgetting and imbalanced data issues among newand past classes. Experimental results for four MedMNIST datasets asbenchmark public datasets and in-house echocardiography cines as thelarge-scale and more complex dataset validate that CCSI outperformsthe state-of-the-art methods in data-free class incremental learningwith an improbable gap of up to 51% accuracy in the final task andget comparable results with the state-of-the-art data-saving rehearsalbased methods. Our proposed method shows the potential to applyincremental learning in many healthcare applications that cannot savedata due to memory constraints or private issues.
在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新颖的无数据类别增量学习框架——CCSI,用于医学图像分类。在CCSI中,我们通过从训练模型中反演并使用类别均值图像初始化来合成类别特定图像。我们探索了一种最近引入的归一化层——CN,以减少在持续训练期间的重写现象,并提出使用冻结的CN时刻进行图像合成的统计正则化。随后,我们继续在新类别和合成图像上进行训练,使用提出的新损失函数,通过缓解新合成图像与旧类别原始图像之间的域偏移,减轻灾难性遗忘和新旧类别之间数据不平衡问题,从而提高合成数据的实用性。对四个MedMNIST数据集作为基准公共数据集和内部心超电影系列作为大型和更复杂的数据集的实验结果验证了,CCSI在无数据类别增量学习中以高达51%的不可思议的准确率差距超越了最先进的方法,并且与最先进的数据保存演练方法取得了可比的结果。我们提出的方法显示了在许多由于内存限制或隐私问题而无法保存数据的医疗应用中应用增量学习的潜力。
Figure
图
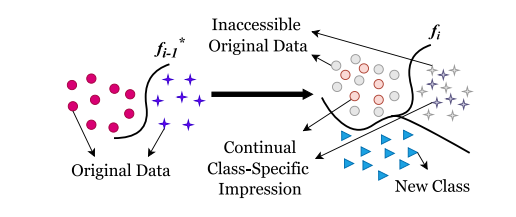
Fig. 1. Representation of data-free class incremental learning. 𝑓𝑖 −1 is the model trainedon previous data, while 𝑓𝑖 is the updated model with new classes. This approach enablesthe incremental learning of new classes added to a previously trained model withouthaving access to previous data. We propose to tackle this problem by synthesizingsamples of previous classes as the continual class-specific impression and adding themto the continual training paradigm. Best viewed in coloured print.
图1. 无数据类别增量学习的表示。𝑓𝑖 −1 是在先前数据上训练的模型,而 𝑓**𝑖 是包含新类别的更新模型。这种方法使得可以在不访问先前数据的情况下,对先前训练的模型进行新类别的增量学习。我们建议通过合成先前类别的样本作为持续类特定印象,并将其添加到持续训练范式中来解决这个问题。彩色打印效果最佳。
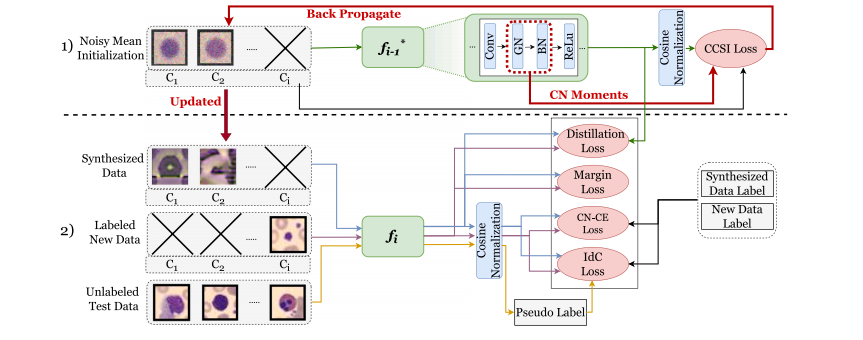
Fig. 2. The class incremental learning pipeline of CCSI. Two main steps of CCSI contain: (1) Continual class-specific data synthesis (Section 3.3): Initialize a batch of images withthe mean of each class to synthesize images using a frozen model trained on the previous task, 𝑓**𝑖 ∗ −1. Update the batch by back-propagating with Eq. (1) and using the statisticssaved in the CN as a regularization term (Eq. (4)); (2) Model update on new tasks (Section 3.4): Leverage information from the previous model using the distillation loss. Toprevent catastrophic forgetting of past tasks, we mitigate domain shift between synthesized and original data with a novel intra-domain conservative (IdC) loss (Section 3.4.1), asemi-supervised domain adaptation technique and encourage robust decision boundaries and overcome data imbalance with the margin loss (Section 3.4.2) and cosine-normalizedcross-entropy (CN-CE) loss (Section 3.4.3). Best viewed in coloured print.
图2. CCSI的类别增量学习流程。CCSI的两个主要步骤包括:(1) 持续类特定数据合成(第3.3节):初始化一批图像,每个类别的图像以其平均值开始,通过使用在先前任务上训练的冻结模型 𝑓**𝑖 ∗ −1 来合成图像。通过反向传播更新图像批次(使用公式(1))并使用CN中保存的统计数据作为正则化项(公式(4));
(2) 新任务的模型更新(第3.4节):使用蒸馏损失从先前模型中获取信息。为了防止灾难性遗忘,我们通过一种新颖的域内保守(IdC)损失(第3.4.1节),一种半监督域适应技术,来缓解合成数据与原始数据之间的域偏移,并通过边缘损失(第3.4.2节)和余弦归一化交叉熵(CN-CE)损失(第3.4.3节)来鼓励稳健的决策边界并克服数据不平衡问题。彩色打印效果最佳。
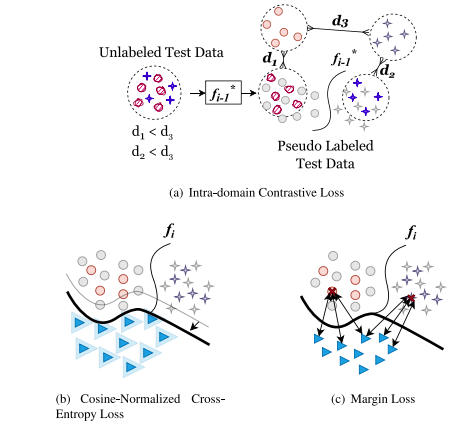
Fig. 3. The effect of each loss on the model’s latent space. 𝑓𝑖 −1 is the model trainedon previous data, and 𝑓𝑖 is the updated model with new classes. (a) The intra-domaincontrastive loss reduces the domain shift by minimizing the distance between thesynthesized and test data of the same class and maximizing the distance betweensynthesized data from different classes. (b) The margin loss enforces the separationbetween the latent representation of the new class and the previously trained classes.(c) The cosine-normalized cross-entropy loss balances the importance of the newclass against the previously trained classes in the latent space to achieve clear classboundaries. Best viewed in coloured print.
图3. 各损失对模型潜在空间的影响。𝑓𝑖 −1 是在先前数据上训练的模型,𝑓𝑖 是包含新类别的更新模型。
(a) 域内对比损失通过最小化同一类别的合成数据和测试数据之间的距离,以及最大化不同类别的合成数据之间的距离,来减少域偏移。
(b) 边缘损失强制新类别的潜在表示与先前训练的类别之间的分离。
(c) 余弦归一化交叉熵损失平衡新类别与先前训练的类别在潜在空间中的重要性,以实现清晰的类别边界。彩色打印效果最佳。
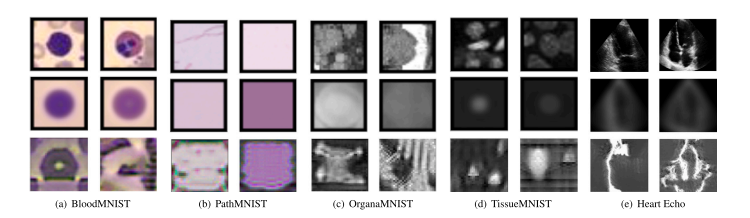
Fig. 4. Datasets’ samples. Each dataset’s first row shows samples from two different classes, the second row is the mean initialization of the respective class, and the third row isthe synthesized images. Best view in coloured.
图4. 数据集样本。每个数据集的第一行显示来自两个不同类别的样本,第二行是相应类别的平均初始化图像,第三行是合成图像。彩色查看效果最佳。
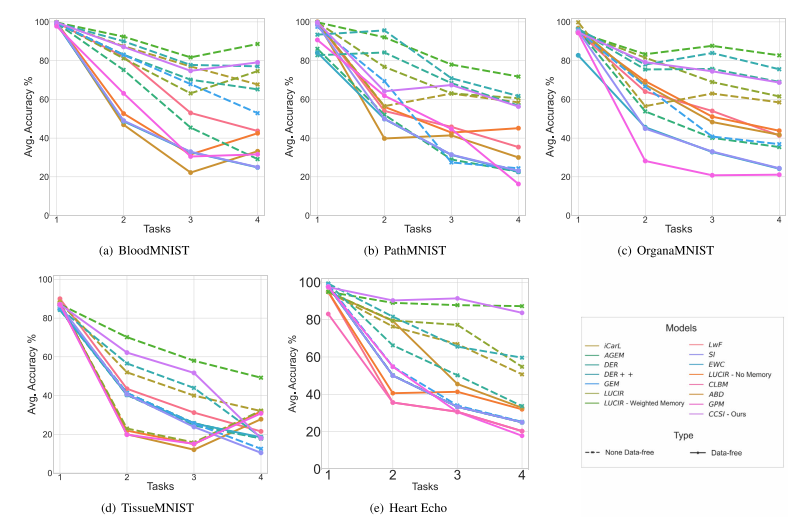
Fig. 5. Testing accuracies on all tasks compared with state-of-the-art class-incremental learning. Dashed lines represent non-data-free methods, while straight lines representdata-free methods. We outperform all data-free methods on all datasets except TissueMNIST. While we surpass some non-data-free methods, we achieve comparable results withothers.
图5. 在所有任务上的测试准确率与最先进的类别增量学习方法的比较。虚线表示非无数据方法,而实线表示无数据方法。除了TissueMNIST数据集外,我们在所有数据集上均超越了所有无数据方法。虽然我们超越了一些非无数据方法,但我们与其他方法取得了可比的结果。
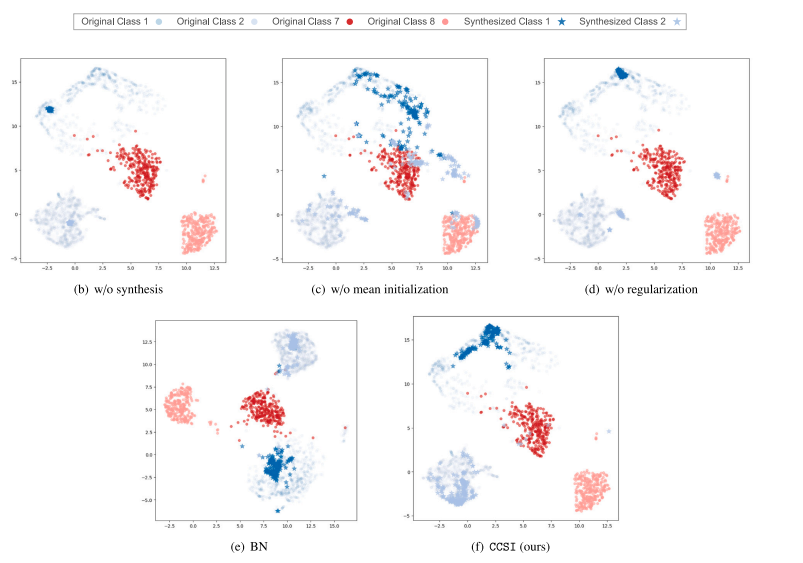
Fig. 6. Visual representations of both original and synthesized images for the BloodMNIST dataset in the latent space, utilizing various methods for the synthesis step usingUMAP (McInnes et al., 2018). We aim to show that the synthetic data generated via CCSI has the closest distribution with the original ones compared with alternatives. Wepresent the latent space representation of original samples from previous classes: the initial two classes (1 and 2), and current classes: the two most recently added classes (7 and8in the final task, using circle markers (∙). In addition, we showcase synthesized samples for the initial two classes, represented by star markers (⋆), which serve as exemplarsof original samples that are no longer available
图6. 使用UMAP(McInnes等人,2018)在潜在空间中可视化BloodMNIST数据集的原始图像和合成图像,采用各种方法进行合成步骤。我们旨在展示通过CCSI生成的合成数据与原始数据相比分布最接近。我们展示了来自先前类别的原始样本的潜在空间表示:初始两个类别(1和2),以及当前类别:最终任务中最近添加的两个类别(7和8),使用圆形标记(∙)。此外,我们展示了初始两个类别的合成样本,使用星形标记(⋆)表示,这些样本作为不再可用的原始样本的典范。
Table
表
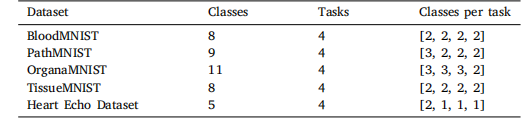
Table 1Class division for MedMNIST and Heart Echo datasets. In each task, we introducedifferent classes than previously learned tasks. Our goal is to have a model performingwell in all of the introduced classes.
表1MedMNIST和心脏回声数据集的类别划分。在每个任务中,我们引入了与先前学习任务不同的类别。我们的目标是让模型在所有引入的类别中表现良好。
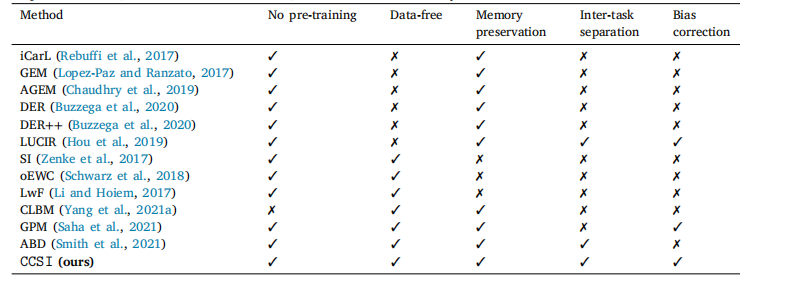
Table 2Conceptual comparison of CCSI and state-of-the-art class incremental learning methods. CCSI is a data-free approach thatsynthesizes data without pre-training using additional data. Moreover, we leverage the synthesized data to retain the memoryof previous classes, address inter-task confusion, and overcome task-recency bias.
表2CCSI与最先进的类别增量学习方法的概念比较。CCSI是一种无数据的方法,通过合成数据而无需使用额外数据进行预训练。此外,我们利用合成数据保留对先前类别的记忆,解决任务间混淆问题,并克服任务最近性偏差。

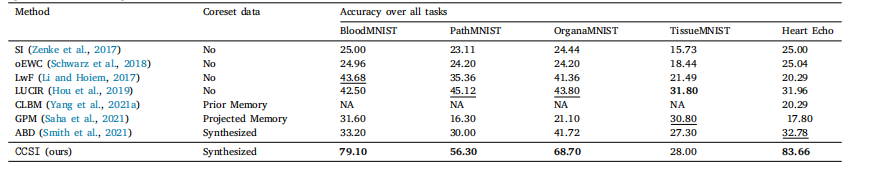
Table 3Testing accuracies of final task over MedMNIST and Heart Echo datasets compared with data-free baselines of class-incremental learning. CCSI shows consistently higher accuracy,up to 51% increase compared to the state-of-the-art data-free methods.
表3MedMNIST和Heart Echo数据集上最终任务的测试准确率,与无数据类别增量学习基线方法的比较。CCSI显示出始终更高的准确率,相较于最先进的无数据方法提高了高达51%。
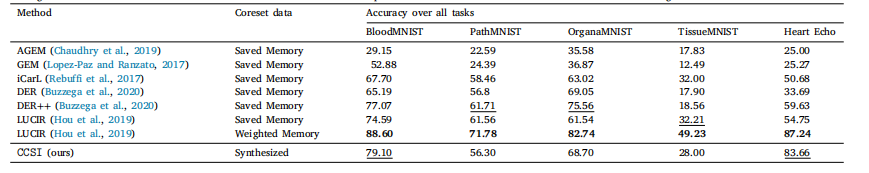
Table 4Testing accuracies of final task over MedMNIST and Heart Echo datasets compared with non-data-free baselines of class-incremental learning.
表4MedMNIST和Heart Echo数据集上最终任务的测试准确率,与非无数据类别增量学习基线方法的比较。
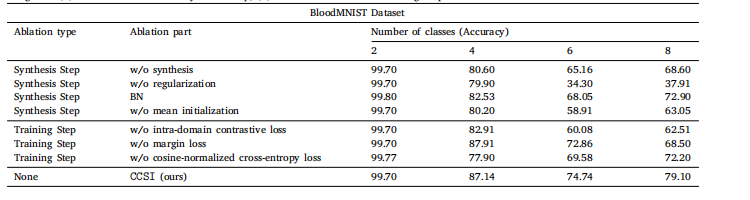
Table 5Testing accuracy of ablation studies done on different configurations of the proposed framework. These experiments are divided into two maincategories: (1) Modifications over the synthesis Step; (2) Modifications over the training Step.
表5对所提出框架不同配置进行消融研究的测试准确率。这些实验分为两大类:(1) 对合成步骤的修改;(2) 对训练步骤的修改。