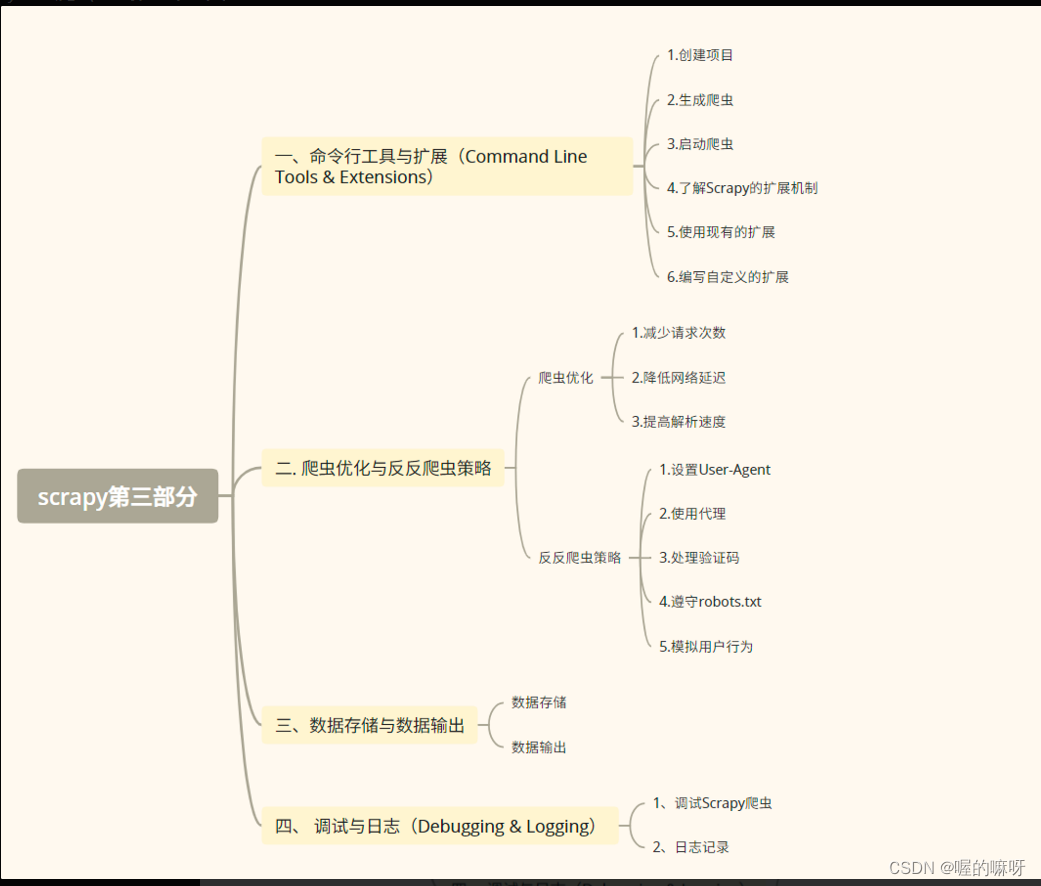
为什么要有过期策略?
Redis是一个内存型的数据库,数据是放在内存里的,但是内存也是有大小的,所以,需要配置redis占用的最大内存,主要通过maxmemory配置
maxmomory <bytes> # redis占用的最大内存
官网:https://redis.io/docs/manual/eviction/ 介绍
For example, to configure a memory limit of 100 megabytes, you can use the following directive inside the redis.conf file:
maxmomory 100mbSetting maxmemory to zero results into no memory limits. This is the default behavior for 64 bit systems, while 32 bit systems use an implicit memory limit of 3GB.
翻译一下,大致意思是如果配置为0,那么模式最大内存大小就是电脑的内存,如果是32bit隐式大小就是3G。
如果我们不淘汰过期的key数据,堆积到一定程度,就会占满内存,满了,就不能再放数据,所以我们需要key过期机制,去删除过期的数据,保证redis的高可用。
什么是Redis key过期策略?
我们知道redis有一个特性,redis中的数据,我们都是可以设置过期时间的,如果时间到了,这个数据就会从Redis中移除。那么redis key的过期策略就是我们怎么将redis中的过期数据移除。
key的惰性过期策略
惰性过期,就是在redis里面,在每次访问操作key的时候,才判断这个key是否过期了,如果过期了就删除数据。redis中主要是通过db.c的expireIfNeeded方法去判断,调用到相关命令时才会去调用,平时不会去判断是否过期
查看一下源码,expireIfNeeded方法,在db.c源码,基于Redis6.0
int expireIfNeeded(redisDb *db, robj *key) {if (!keyIsExpired(db,key)) return 0;/* If we are running in the context of a slave, instead of* evicting the expired key from the database, we return ASAP:* the slave key expiration is controlled by the master that will* send us synthesized DEL operations for expired keys.** Still we try to return the right information to the caller,* that is, 0 if we think the key should be still valid, 1 if* we think the key is expired at this time. */// 如果有配置masterhost,说明是从节点,那么不执行key删除操作if (server.masterhost != NULL) return 1;/* Delete the key */server.stat_expiredkeys++;propagateExpire(db,key,server.lazyfree_lazy_expire);notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EXPIRED,"expired",key,db->id);// 判断lazyfree_lazy_expire是否开启,开启执行异步删除,不开启执行同步删除,4.0之后新增的功能,默认是关闭int retval = server.lazyfree_lazy_expire ? dbAsyncDelete(db,key) :dbSyncDelete(db,key);if (retval) signalModifiedKey(NULL,db,key);return retval;
}
惰性删除策略可以节省CPU资源,因为只需要访问key的时候才去判断是否过期,所以平时是没啥CPU损耗的,但是如果没有再次访问,改过期的key就一直堆积在内存里面,不会被清除,从而占用大量内存空间,所以我们需要另外一种策略来配合使用,解决内存占用问题,就是下面说的key定时过期策略。
key的定期过期策略
Redis中也提供了定期清除过期key的策略,在redis源码里的server.c,里面有个serverCron方法,这个方法除了做Rehash以外,还会做很多其他的操作,比如
- 清理数据库中的过期键值对
- 关闭和清理连接失效的客户端
- 尝试进行持久化操作
- 更新服务器的各类统计信息(时间、内存占用、数据库占用情况等)
Redis多久去清除过期的数据,执行频率根据redis.conf里的配置hz

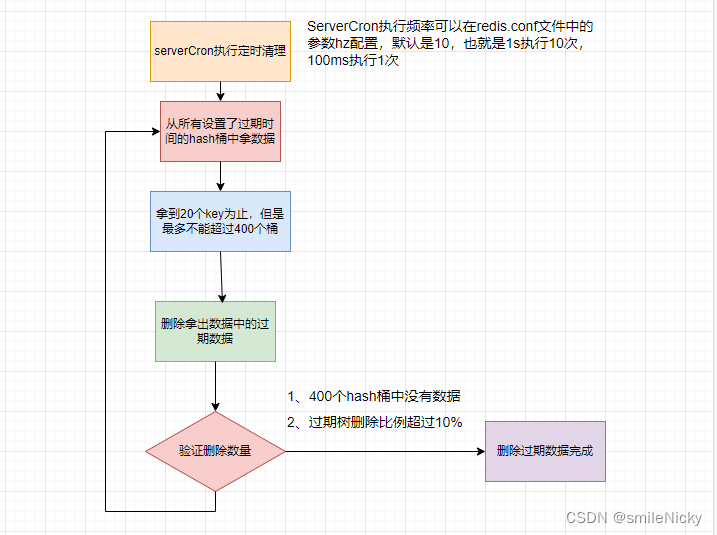
然后实现流程大概是咋样的?具体实现流程如下:
-
serverCron方法去执行定时清理,执行频率redis.conf的hz参数配置,默认是10,也就是1s执行10次,100ms执行1次 -
执行清理的时候,去扫描所有设置了过期时间的key,不会去扫描所有的key
-
根据桶的维度去扫描key,直到扫到20个key(可配)且最多取400个桶。假如第一个桶是15个key,没有达到20个key,所以会继续扫描第二个桶,第二个桶20个key,由于是以桶为维度进行扫描的,第二个桶会被全部扫描,所以总共扫描了35个key
-
找到扫描的key里面过期的key,进行删除操作
-
判断扫描的过期数据跟扫描总数的比例是否超过10%,是,继续执行3、4步;否,删除完成。
执行过程,画一个流程图:
查看源码,验证一下,在redis源码里的server.c有一个serverCron方法,里面有个databasesCron函数
/* Handle background operations on Redis databases. */
databasesCron();
同个类里,查看databasesCron函数
void databasesCron(void) {/* Expire keys by random sampling. Not required for slaves* as master will synthesize DELs for us. */if (server.active_expire_enabled) {if (iAmMaster()) { // 是否主服务器activeExpireCycle(ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW);} else { // 从服务器expireSlaveKeys();}}/* Defrag keys gradually. */activeDefragCycle();/* Perform hash tables rehashing if needed, but only if there are no* other processes saving the DB on disk. Otherwise rehashing is bad* as will cause a lot of copy-on-write of memory pages. */if (!hasActiveChildProcess()) {/* We use global counters so if we stop the computation at a given* DB we'll be able to start from the successive in the next* cron loop iteration. */static unsigned int resize_db = 0;static unsigned int rehash_db = 0;int dbs_per_call = CRON_DBS_PER_CALL;int j;/* Don't test more DBs than we have. */if (dbs_per_call > server.dbnum) dbs_per_call = server.dbnum;/* Resize */for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call; j++) {tryResizeHashTables(resize_db % server.dbnum);resize_db++;}/* Rehash */if (server.activerehashing) {for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call; j++) {int work_done = incrementallyRehash(rehash_db);if (work_done) {/* If the function did some work, stop here, we'll do* more at the next cron loop. */break;} else {/* If this db didn't need rehash, we'll try the next one. */rehash_db++;rehash_db %= server.dbnum;}}}}
}
查看activeExpireCycle方法,在expire.c
void activeExpireCycle(int type) {/* Adjust the running parameters according to the configured expire* effort. The default effort is 1, and the maximum configurable effort* is 10. */unsigned longeffort = server.active_expire_effort-1, /* Rescale from 0 to 9. */config_keys_per_loop = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_KEYS_PER_LOOP +ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_KEYS_PER_LOOP/4*effort,config_cycle_fast_duration = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION +ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION/4*effort,config_cycle_slow_time_perc = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC +2*effort,config_cycle_acceptable_stale = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_ACCEPTABLE_STALE-effort;/* This function has some global state in order to continue the work* incrementally across calls. */static unsigned int current_db = 0; /* Last DB tested. */static int timelimit_exit = 0; /* Time limit hit in previous call? */static long long last_fast_cycle = 0; /* When last fast cycle ran. */int j, iteration = 0;int dbs_per_call = CRON_DBS_PER_CALL;long long start = ustime(), timelimit, elapsed;/* When clients are paused the dataset should be static not just from the* POV of clients not being able to write, but also from the POV of* expires and evictions of keys not being performed. */if (clientsArePaused()) return;if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST) {/* Don't start a fast cycle if the previous cycle did not exit* for time limit, unless the percentage of estimated stale keys is* too high. Also never repeat a fast cycle for the same period* as the fast cycle total duration itself. */if (!timelimit_exit &&server.stat_expired_stale_perc < config_cycle_acceptable_stale)return;if (start < last_fast_cycle + (long long)config_cycle_fast_duration*2)return;last_fast_cycle = start;}/* We usually should test CRON_DBS_PER_CALL per iteration, with* two exceptions:** 1) Don't test more DBs than we have.* 2) If last time we hit the time limit, we want to scan all DBs* in this iteration, as there is work to do in some DB and we don't want* expired keys to use memory for too much time. */if (dbs_per_call > server.dbnum || timelimit_exit)dbs_per_call = server.dbnum;/* We can use at max 'config_cycle_slow_time_perc' percentage of CPU* time per iteration. Since this function gets called with a frequency of* server.hz times per second, the following is the max amount of* microseconds we can spend in this function. */timelimit = config_cycle_slow_time_perc*1000000/server.hz/100;timelimit_exit = 0;if (timelimit <= 0) timelimit = 1;if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST)timelimit = config_cycle_fast_duration; /* in microseconds. *//* Accumulate some global stats as we expire keys, to have some idea* about the number of keys that are already logically expired, but still* existing inside the database. */long total_sampled = 0;long total_expired = 0;for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call && timelimit_exit == 0; j++) {/* Expired and checked in a single loop. */unsigned long expired, sampled;redisDb *db = server.db+(current_db % server.dbnum);/* Increment the DB now so we are sure if we run out of time* in the current DB we'll restart from the next. This allows to* distribute the time evenly across DBs. */current_db++;/* Continue to expire if at the end of the cycle there are still* a big percentage of keys to expire, compared to the number of keys* we scanned. The percentage, stored in config_cycle_acceptable_stale* is not fixed, but depends on the Redis configured "expire effort". */do {unsigned long num, slots;long long now, ttl_sum;int ttl_samples;iteration++;/* If there is nothing to expire try next DB ASAP. */if ((num = dictSize(db->expires)) == 0) {db->avg_ttl = 0;break;}slots = dictSlots(db->expires);now = mstime();/* When there are less than 1% filled slots, sampling the key* space is expensive, so stop here waiting for better times...* The dictionary will be resized asap. */if (num && slots > DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE &&(num*100/slots < 1)) break;/* The main collection cycle. Sample random keys among keys* with an expire set, checking for expired ones. */expired = 0;sampled = 0;ttl_sum = 0;ttl_samples = 0;// 最多那20个if (num > config_keys_per_loop)num = config_keys_per_loop;/* Here we access the low level representation of the hash table* for speed concerns: this makes this code coupled with dict.c,* but it hardly changed in ten years.** Note that certain places of the hash table may be empty,* so we want also a stop condition about the number of* buckets that we scanned. However scanning for free buckets* is very fast: we are in the cache line scanning a sequential* array of NULL pointers, so we can scan a lot more buckets* than keys in the same time. */long max_buckets = num*20;long checked_buckets = 0;// 如果拿到的key数量大于20 或者 checked_buckets大于400,跳出循环while (sampled < num && checked_buckets < max_buckets) {for (int table = 0; table < 2; table++) {if (table == 1 && !dictIsRehashing(db->expires)) break;unsigned long idx = db->expires_cursor;idx &= db->expires->ht[table].sizemask;// 根据index拿到hash桶dictEntry *de = db->expires->ht[table].table[idx];long long ttl;/* Scan the current bucket of the current table. */checked_buckets++;// 循环hash桶里的keywhile(de) {/* Get the next entry now since this entry may get* deleted. */dictEntry *e = de;de = de->next;ttl = dictGetSignedIntegerVal(e)-now;if (activeExpireCycleTryExpire(db,e,now)) expired++;if (ttl > 0) {/* We want the average TTL of keys yet* not expired. */ttl_sum += ttl;ttl_samples++;}sampled++;}}db->expires_cursor++;}total_expired += expired;total_sampled += sampled;/* Update the average TTL stats for this database. */if (ttl_samples) {long long avg_ttl = ttl_sum/ttl_samples;/* Do a simple running average with a few samples.* We just use the current estimate with a weight of 2%* and the previous estimate with a weight of 98%. */if (db->avg_ttl == 0) db->avg_ttl = avg_ttl;db->avg_ttl = (db->avg_ttl/50)*49 + (avg_ttl/50);}/* We can't block forever here even if there are many keys to* expire. So after a given amount of milliseconds return to the* caller waiting for the other active expire cycle. */if ((iteration & 0xf) == 0) { /* check once every 16 iterations. */elapsed = ustime()-start;if (elapsed > timelimit) {timelimit_exit = 1;server.stat_expired_time_cap_reached_count++;break;}}/* We don't repeat the cycle for the current database if there are* an acceptable amount of stale keys (logically expired but yet* not reclaimed). */// 比例超过10%,expired过期的key数量,sampled总的扫描数量} while (sampled == 0 ||(expired*100/sampled) > config_cycle_acceptable_stale);}elapsed = ustime()-start;server.stat_expire_cycle_time_used += elapsed;latencyAddSampleIfNeeded("expire-cycle",elapsed/1000);/* Update our estimate of keys existing but yet to be expired.* Running average with this sample accounting for 5%. */double current_perc;if (total_sampled) {current_perc = (double)total_expired/total_sampled;} elsecurrent_perc = 0;server.stat_expired_stale_perc = (current_perc*0.05)+(server.stat_expired_stale_perc*0.95);
}