上一篇我们一起学习了
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext介绍AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 。
【spring】AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 类学习_annotationconfigapplicationcontext方法-CSDN博客
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext是一个用于加载和刷新基于XML配置文件的应用程序上下文的类。 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext类继承自AbstractApplicationContext,实现了ApplicationContext接口。它提供了一种在文件系统上查找和加载XML配置文件的方式,这使得开发者可以轻松地管理和更新应用程序的配置。 使用FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的步骤通常如下:
- 创建一个配置文件路径的列表,这些路径指向应用程序的XML配置文件。
- 创建
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext实例,将配置文件路径列表作为构造函数参数传入。 - 调用
refresh()方法来启动Spring容器,加载和处理配置文件,初始化和注册bean。 - 通过调用
getBean()方法从应用程序上下文中获取bean,并使用它们构建应用程序。
源码截图
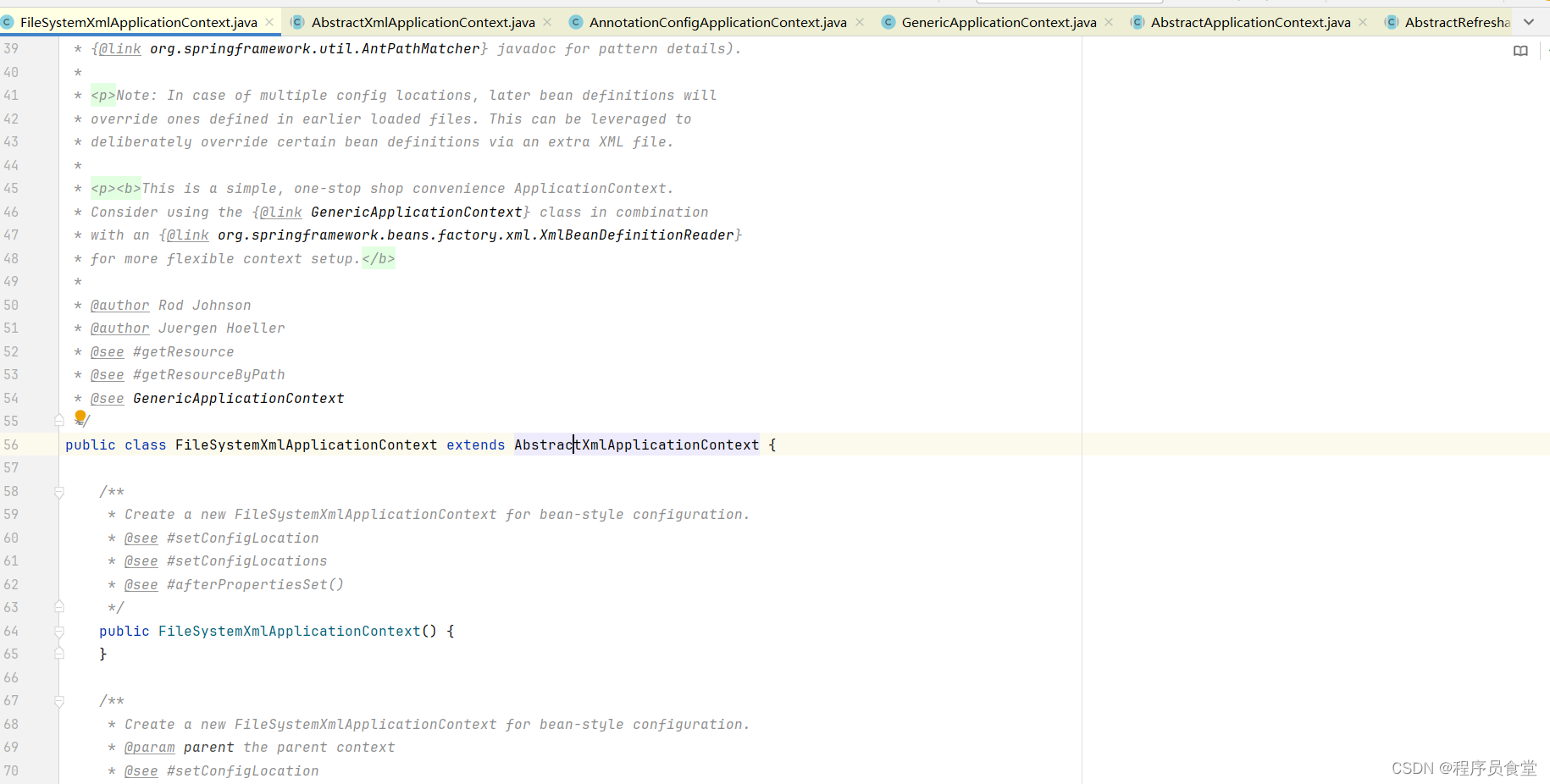
构造函数源代码
/*** 单配置文件加载* configLocation 包含了 BeanDefinition 所在的文件路径** @param configLocation* @throws BeansException*/public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext (String configLocation) throws BeansException {this (new String[]{configLocation}, true, null);}/*** 多配置文件加载* 可以定义多个 BeanDefinition 所在的文件路径** @param configLocations* @throws BeansException*/public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext (String... configLocations) throws BeansException {this (configLocations, true, null);}/*** 类路径和文件系统混合加载* 在定义多个 BeanDefinition 所在的文件路径 的同时,还能指定自己的双亲 IoC 容器** @param configLocations* @param parent* @throws BeansException*/public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext (String[] configLocations, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {this (configLocations, true, parent);}public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext (String[] configLocations, boolean refresh) throws BeansException {this (configLocations, refresh, null);}/*** 如果应用直接使用 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 进行实例化,则都会进到这个构造方法中来*/public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext (String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)throws BeansException {// 动态地确定用哪个加载器去加载我们的配置文件super (parent);// 告诉读取器 配置文件放在哪里,该方法继承于爷类 AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContextsetConfigLocations (configLocations);if (refresh) {// 容器初始化refresh ();}}/*** 实例化一个 FileSystemResource 并返回,* 本方法是在其父类 DefaultResourceLoader的getResource 方法中被调用的,*/@Overrideprotected Resource getResourceByPath (String path) {if (path != null && path.startsWith ("/")) {path = path.substring (1);}return new FileSystemResource (path);}FileSystemXmlApplicationContext (String configLocation)
参数:configLocation(String类型),这是XML配置文件的路径。它可以根据提供的路径加载单个或多个XML配置文件。如果路径包含逗号分隔的字符串,那么它将加载所有指定的配置文件。
示例代码:
ApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("path/spring-config.xml");FileSystemXmlApplicationContext (String... configLocations)
参数:configLocations(String数组类型),这是一个包含多个XML配置文件路径的数组。它会加载数组中指定的所有配置文件。
示例代码:
ApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(new String[] {"path/spring-config1.xml", "path/spring-config2.xml"});FileSystemXmlApplicationContext (String[] configLocations, ApplicationContext parent)
这个构造函数除了接受一组配置文件位置外,还接受一个父级ApplicationContext对象。这样可以创建一个具有父子上下文关系的层次结构,子上下文可以从父上下文中继承配置和共享Bean。
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext (String[] configLocations, boolean refresh)
它允许开发者指定一个配置文件路径数组和一个刷新标志来创建一个应用程序上下文实例。
String[] configLocations: 这是一个字符串数组,包含了要加载的Spring配置文件的路径。这些路径可以是文件系统中的绝对路径或相对路径,也可以是URL。数组中的每个元素都是一个有效的文件路径,上下文将会尝试加载这些路径指向的配置文件。boolean refresh: 这是一个布尔值,指示是否在创建上下文实例后立即刷新上下文。如果设置为true,那么在构造函数执行完毕后,上下文会自动调用refresh()方法,这将触发上下文的初始化过程,包括加载配置文件、解析Bean定义、注册Bean以及执行任何初始化相关的回调。
示例代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {try {// 定义Spring配置文件的路径数组String[] configLocations = {"file:/path/spring-config1.xml","file:/path/spring-config2.xml"};// 创建FileSystemXmlApplicationContext实例// 这里设置refresh为true,表示在创建上下文后立即刷新上下文ApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(configLocations, true);// 从上下文中获取Bean实例DemoBean demoBean= (DemoBean) context.getBean("demoBean");// 使用获取到的demoBeandemoBean.test();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext (String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
这个构造函数提供了最大的灵活性。它允许你指定是否在创建上下文后立即刷新上下文(这将加载所有的bean定义并启动上下文的生命周期),以及是否指定一个父上下文。
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext通过调用其父类AbstractApplicationContext的 refresh() 函数启动整个IOC容器对Bean定义的载入过程,下一篇我们好好聊聊。Spring IOC容器对Bean定义资源的载入是从refresh()函数开始的,refresh()是一个模板方法,refresh()方法的作用是:
在创建IOC容器前,如果已经有容器存在,则需要把已有的容器销毁和关闭,以保证在refresh之后使用的是新建立起来的IOC容器。
refresh的作用类似于对IOC容器的重启,在新建立好的容器中对容器进行初始化,对Bean定义资源进行载入。