四 . 分支和循环
1 . switch的基本语法
if 和 swicth 的对比:
- if既可以用于范围校验, 也可以用于等值校验
- swicth对于if效率更高,只能用于等值校验
语法格式:
switch(表达式){case 常量值1:语句块1;//break;case 常量值2:语句块2;//break; // ...[default:语句块n+1;break;]
}
注意:1. Switch用于等值校验2. break结束分支3.default可有可无, 所有的case都不满足时,就会执行public class SwitchTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//1,创建键盘输入对象Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);//2,获取整数System.out.println("请您输入一个整数");int num = in.nextInt();//3,对整数进行判断switch(num){case 1:System.out.println("11");break;case 2:System.out.println("22");break;case 3:System.out.println("33");break;default:System.out.println("输入有误!");break;}//4,输出//5,关闭资源in.close();}
}
2 . switch支持的数据类
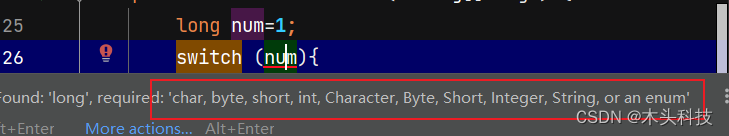
switch表达式的数据类型----------------byte short int char String 枚举,,,不支持long
class SwitchTest2{public static void main(String[] args) {//键盘输入一个季节,展示当前季节的特点//1,创建键盘输入对象Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);//2,获取System.out.println("请您输入一个季节:");//类型是String的话,后面用next()String arr = in.next();//3,判断switch(arr){case "春天":System.out.println("春天好呀");break;case "夏天":System.out.println("夏天好呀");break;case "秋天":System.out.println("秋天好呀");break;case"冬天":System.out.println("冬天好呀");break;default:System.out.println("你输入的不是季节");break;}//4,输出//5,关闭资源in.close();}}
-------键盘输入年份和月份 输出制定月份的天数
/*
switch练习
1.键盘输入年份和月份 输出制定月份的天数*/
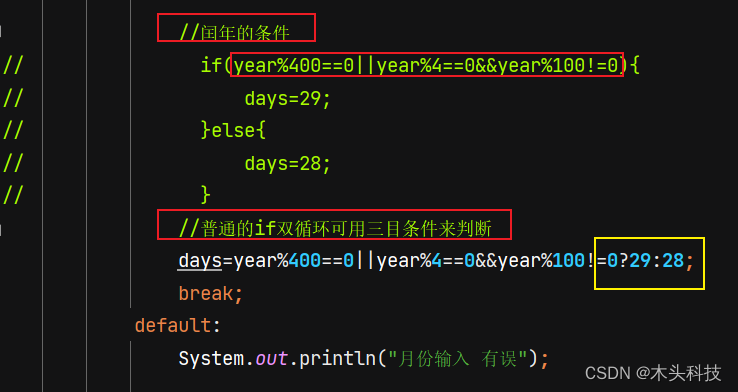
public class SwitchExer {public static void main(String[] args) {//1.创建键盘输入Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);//2,获取System.out.println("请您输入年份");int year=in.nextInt();System.out.println("请您输入月份");int month=in.nextInt();//3,定义变量 接受天数的值int days=0;//4,月份进行校验,特别处理2月switch(month){case 1:case 3:case 5:case 7:case 8:case 10:case 12:days=31;break;case 4:case 6:case 9:case 11:days=30;break;case 2://闰年的条件
// if(year%400==0||year%4==0&&year%100!=0){
// days=29;
// }else{
// days=28;
// }//普通的if双循环可用三目条件来判断days=year%400==0||year%4==0&&year%100!=0?29:28;break;default:System.out.println("月份输入 有误");}//5,展示System.out.println(year+"年"+month+"月"+days+"天");//6,关闭in.close();}
}
3.循环语句
循环语句就是解决重复性问题
-
循环的作用:循环语句具有在
某些条件满足的情况下,反复执行特定代码的功能。 -
循环结构分类:
- for 循环
- while 循环
- do-while 循环
-
循环结构
四要素:- 初始化条件
- 循环条件
- 循环体
- 迭代条件
4.for循环
基本语法
for (①初始化条件; ②循环条件; ④迭代条件){③循环体;
}
**执行过程:**①-②-③-④-②-③-④-②-③-④-…-②
①初始化条件: 循环的起始值
②循环条件: 判断循环是否执行的条件
③循环体: 循环做的事
④迭代条件: 更改起始值
i++和++i一样,习惯问题
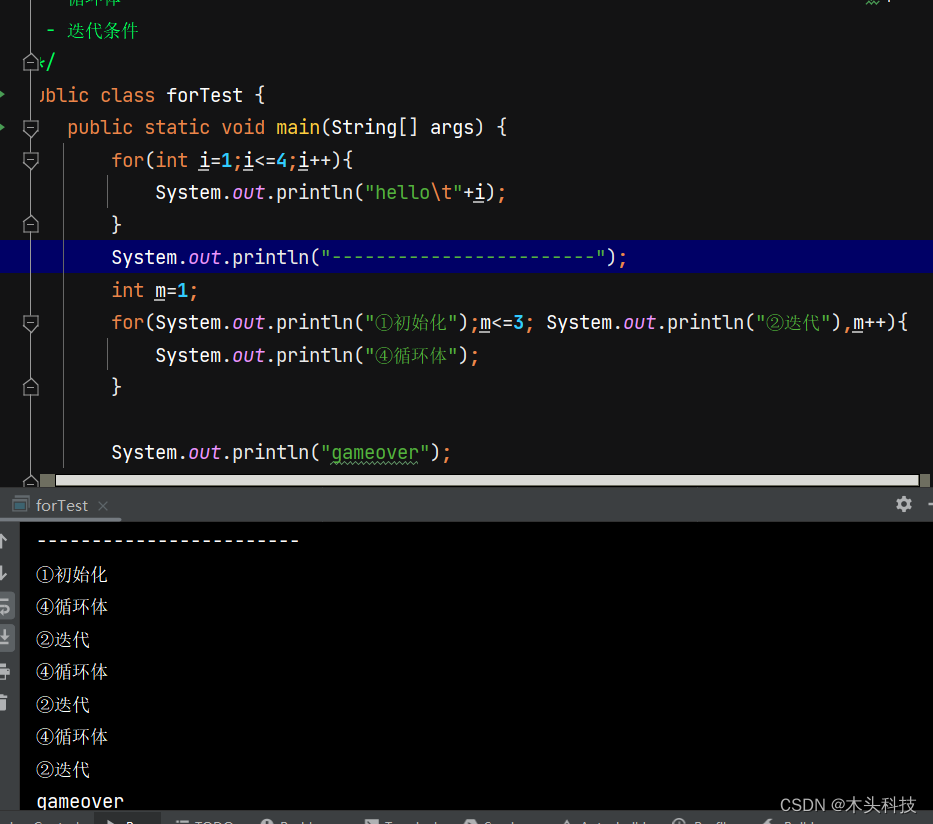
注意 :如果需要变量记录数据, 思考变量的位置循环外: 记录总变化(循环结束后才能拿到最终结果)循环内:
1. 如果需要变量记录数据, 思考变量的位置循环外: 记录总变化(循环结束后才能拿到最终结果)循环内:
2. for中声明的变量, 外部无法使用(可以把初始化条件调到外面)
3. 特殊的写法缺少循环条件 无限循环缺少迭代条件 无限循环只有循环体 无限循环无限循环下 不能存在其他内容 无法访问
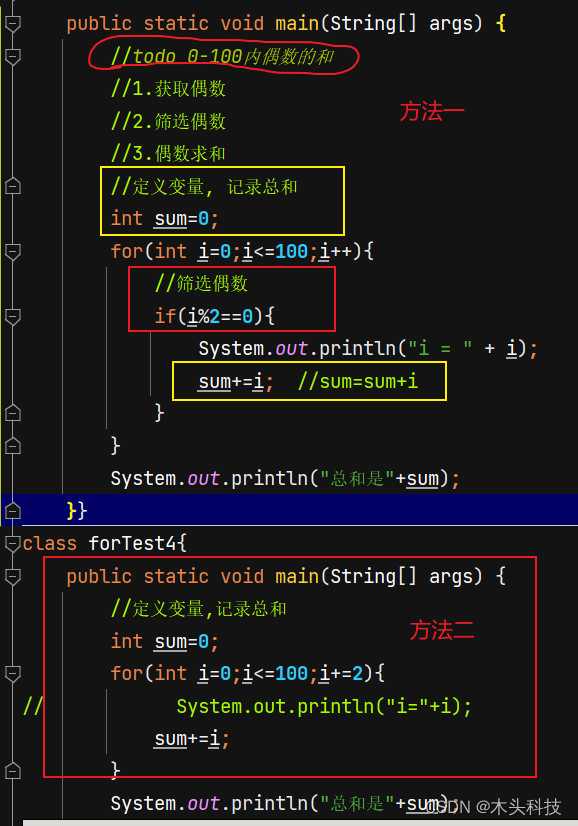
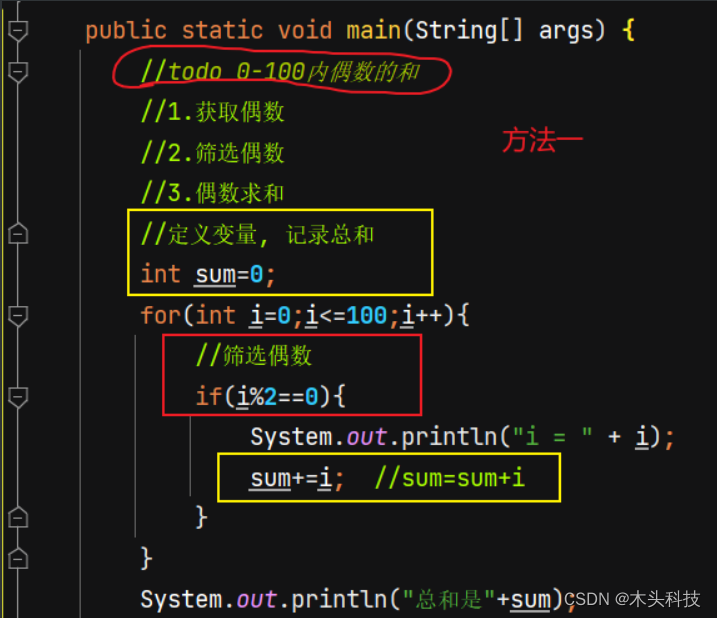
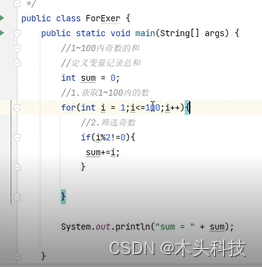
5.偶数. 奇数
判断偶数: i%2==0
判断奇数: i%2!==0
6 .while循环
语法格式:
①初始化部分
while(②循环条件部分){③循环体部分;④迭代部分;
}
**执行过程:**①-②-③-④-②-③-④-②-③-④-…-②
练习----展示1-200内能被3整除的所有数, 每行输出5个
class While4{public static void main(String[] args) {//展示1-200内能被3整除的所有数, 每行输出5个//定义变量能被3整数的数量int count=0;//1.所有的数for (int i = 1; i <=200 ; i++) {//2.筛选被3整除的数if(i%3==0){System.out.println(i+"\t");count++;if(count%5==0){System.out.println();}}}}
}
练习----找产生幸运数字 [1,1000] 666
*/
class While5{public static void main(String[] args) {//幸运数字公式int yy=(int)(Math.random()*(1000-1+1)+1);//1.`确定幸运数字//2,键盘输入Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);//这个num在范围外的目的是为了接受所输入的数字//只要这个num与幸运数字不一样,就会不断地寻找int num=-1;while(num!=yy){System.out.println("输入数字");num=in.nextInt();//输入的数字与幸运数字比较if(num>yy){System.out.println("大了");} else if (num < yy) {System.out.println("笑了");}else{System.out.println("找到了,幸运数字是:"+num+",yy"+yy);}}
// System.out.println("输入一个数字");
// int num = in.nextInt();
// if(num>yy){
// System.out.println("大了");
// } else if (num<yy) {
// System.out.println("笑了");
// }else{
// System.out.println("找到了");
// }}
}
7. do-while循环
语法格式:
①初始化部分;
do{③循环体部分④迭代部分
}while(②循环条件部分);
**执行过程:**①-③-④-②-③-④-②-③-④-…-②
public class d0while {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建初始化int i=1;do{System.out.println("i="+i);i++;}while (i<=5);}
}
for:循环次数固定
while: 循环次数不固定
do while:即使初始化 条件不满足循环条件也会执行一次循环体
return: 结束方法, 跳出程序