练习一:
使用 四种方式拷贝文件,并统计各自用时
1字节流的基本流:一次读写一个字节
2字节流的基本流:一次读写一个字节数组
3字节缓冲流:一次读写一个字节
4字节缓冲流:一次读写一个字节数组
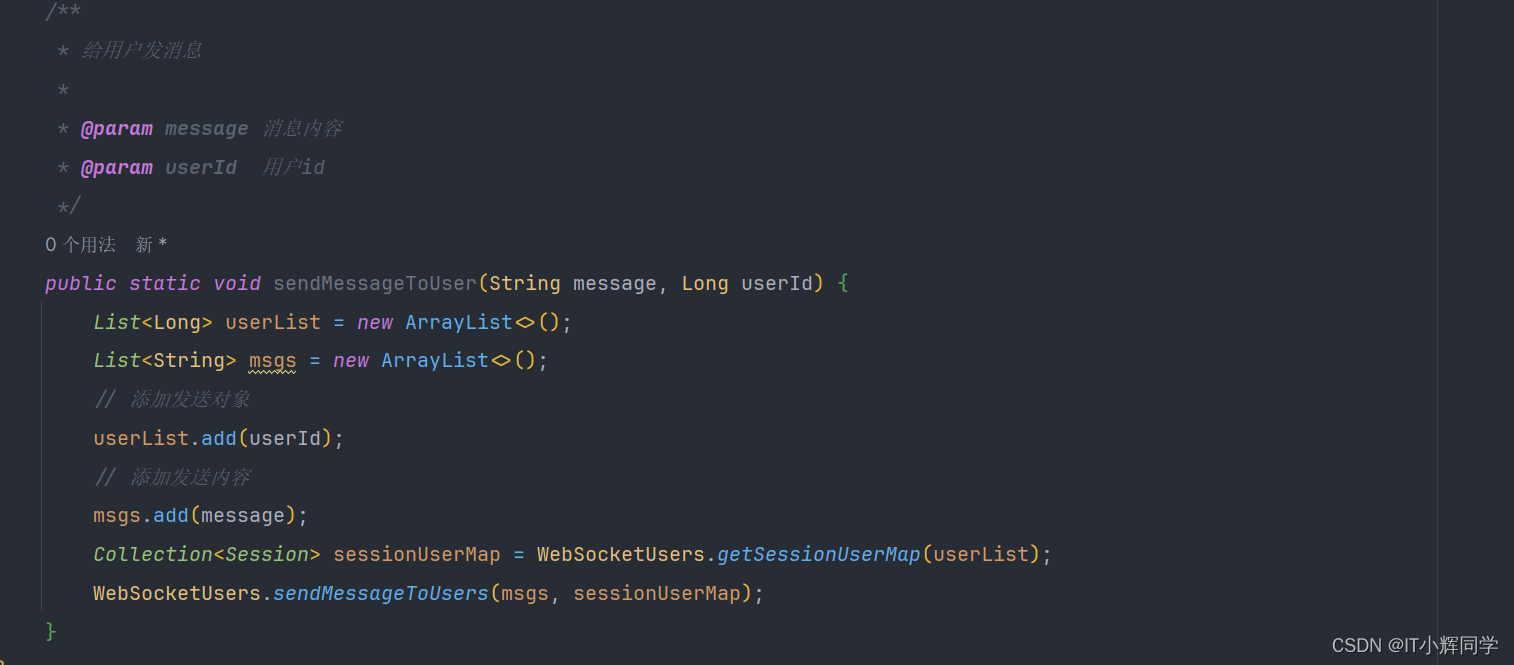
public class Test03 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {/*** 字节流的基本流:一次读写一个字节*/File f1=new File("..\\ioDemo\\a.txt");File f2=new File("..\\ioDemo\\copy3.txt");long start = System.currentTimeMillis();copy(f1, f2);long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println((end-start)/1000.0+"秒");}private static void copy(File f1, File f2) throws IOException {//拷贝使用ioFileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(f1);FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(f2);int b;//read读取的返回值,十进制数while((b=fis.read())!=-1){fos.write(b);}fos.close();fis.close();}
}public class Test04 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {/*** 字节流的基本流:一次读写一个字节数组*/File f1 = new File("..\\ioDemo\\a.txt");File f2 = new File("..\\ioDemo\\copy4.txt");long start = System.currentTimeMillis();copy(f1, f2);long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println((end - start) / 1000.0 + "秒");}private static void copy(File f1, File f2) throws IOException {//拷贝使用ioFileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f1);FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f2);byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int len;//read读取的返回值,十进制数while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {fos.write(bytes, 0, len);}fos.close();fis.close();}
}public class Test01 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {/*** 字节缓冲流:一次读写一个字节*///操作文件使用FileFile f1 = new File("..\\ioDemo\\a.txt");File f2 = new File("..\\ioDemo\\copy1.txt");long start = System.currentTimeMillis();copy1(f1, f2);long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println((end-start)/1000.0+"秒");}public static void copy1(File f1, File f2) throws IOException {//拷贝使用io//创建字节缓冲输入流BufferedInputStream br = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(f1));//创建字节缓冲输出流BufferedOutputStream bw = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f2));int b;while ((b = br.read()) != -1) {bw.write(b);}bw.close();br.close();}
}public class Test02 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {/*** 字节缓冲流:一次读取一个字节数组*/File f1 = new File("..\\ioDemo\\a.txt");File f2 = new File("..\\ioDemo\\copy2.txt");long start = System.currentTimeMillis();copy(f1, f2);long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println((end-start)/1000.0+"秒");}private static void copy(File f1, File f2) throws IOException {//拷贝使用io//创建字节缓冲输入流BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(f1));//创建字节缓冲输出流BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f2));//读取并写入byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];//一次读取1024个字节int len;//一次读取的字节长while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {bos.write(bytes, 0, len);}bos.close();bis.close();}
}总结:以后用一次读取一个数组的方法最快
练习二:
将已经打乱的《出师表》排序,并放入新文件
csb.txt
方法一:
package csb;import java.io.*;
import java.nio.Buffer;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;public class Test01 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {/*** 1.纯文本* 2.出师表每段一行,可以使用字符缓冲流,的特有方法readLine*/File f1 = new File("..\\ioDemo\\csb.txt");File f2 = new File("..\\ioDemo\\csb2.txt");restore(f1, f2);}private static void restore(File f1, File f2) throws IOException {//先用io将文本读取到内存中BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f1));//用来存读取到的文本ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();String s;while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) {//放入集合list.add(s);}//自定义排序排序,因为每一行的开头是数字,可先获取数字,升序排序list.sort(new Comparator<String>() {@Overridepublic int compare(String o1, String o2) {int i1 = Integer.parseInt(o1.split("\\.")[0]);int i2 = Integer.parseInt(o2.split("\\.")[0]);return i1-i2;}});//遍历集合,放入新文件BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(f2));for (String str : list) {bw.write(str);bw.newLine();//换行}bw.close();br.close();}
}方法二:更简洁
package csb;import 字符输出流底层.T;import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;public class Test02 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {/*** 1.纯文本* 2.出师表每段一行,可以使用字符缓冲流,的特有方法readLine*/File f1 = new File("..\\ioDemo\\csb.txt");File f2 = new File("..\\ioDemo\\csb2.txt");restore(f1, f2);}private static void restore(File f1, File f2) throws IOException {//先用io将文本读取到内存中BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f1));//*treeMap对于(Integer作为键时)可自动排序。数字,可作为键,汉字部分可做为值,TreeMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();String s;while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) {//放入集合//注意点:因为split方法适用于正则表达式,所以使用 . 的时候要转义int key = Integer.parseInt(s.split("\\.")[0]);String value = s.split("\\.")[1];map.put(key, value);}//打印集合,检验是否排序System.out.println(map);//已排序//遍历集合,放入新文件BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(f2));Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> entries = map.entrySet();for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : entries) {String num = entry.getKey().toString();//数字转字符串String value = entry.getValue();bw.write(num + "." + value);//1. ....bw.newLine();//换行}bw.close();br.close();}
}排序前:
排序后:
练习三:
public class Test01 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {/**
* 首先记录次数可以用一个变量记录,但是这个变量不能存储在当前程序中(内存中)
* 可以存储在本地文件中,这样变量就不会随着程序的重启而重置
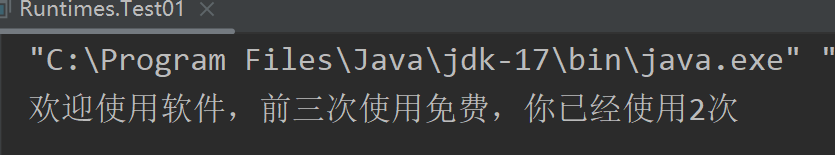
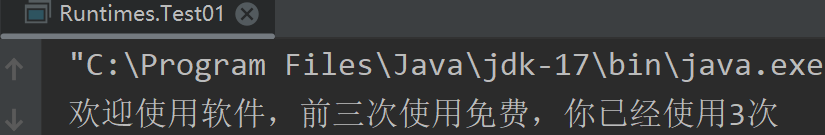
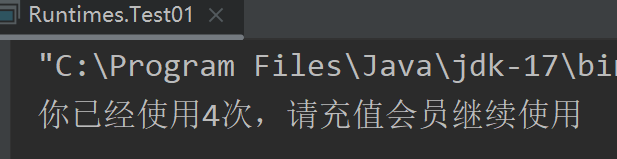
*///创建字符缓冲输入流BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("..\\ioDemo\\store.txt"));//读取数据并转成数字int count = Character.getNumericValue((char) br.read());//第一次获取到0//使用次数加1count++;//1//逻辑if (count <= 3) {System.out.println("欢迎使用软件,前三次使用免费,你已经使用" + count + "次");} else {System.out.println("你已经使用" + count + "次,请充值会员继续使用");}//创建字符缓冲输出流,把更新后的次数写入文件BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("..\\ioDemo\\store.txt"));bw.write(count + "");//将次数变成字符串写入,不然将看作ascii码bw.close();br.close();/*** 注意不要将输出流创建在上面,会清空数据* 注意io流* 随用随创建* 随不用随关闭*/}
}//注意要先将store文件内放入初始值初始0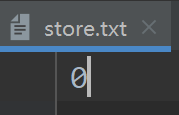
控制台: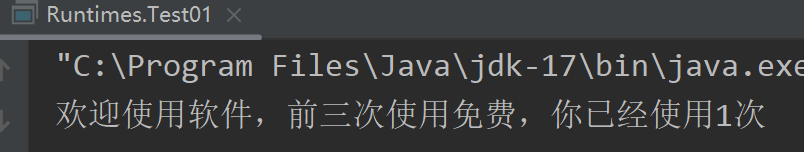


![[职场] 市场总监的简历怎样描述工作经历 #微信#微信#其他](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/828d37d59b617574b27dd1e4cfd71a2e.png)

![[机缘参悟-154] :一个软件架构师对佛学的理解 -19- 宏大的佛教世界观、宇宙观,即系统架构:三千大千世界、佛土、三界、九地、二十五有、六道轮回](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/e89d6df6e8a142ae97c90d16a8ce6dc6.png)