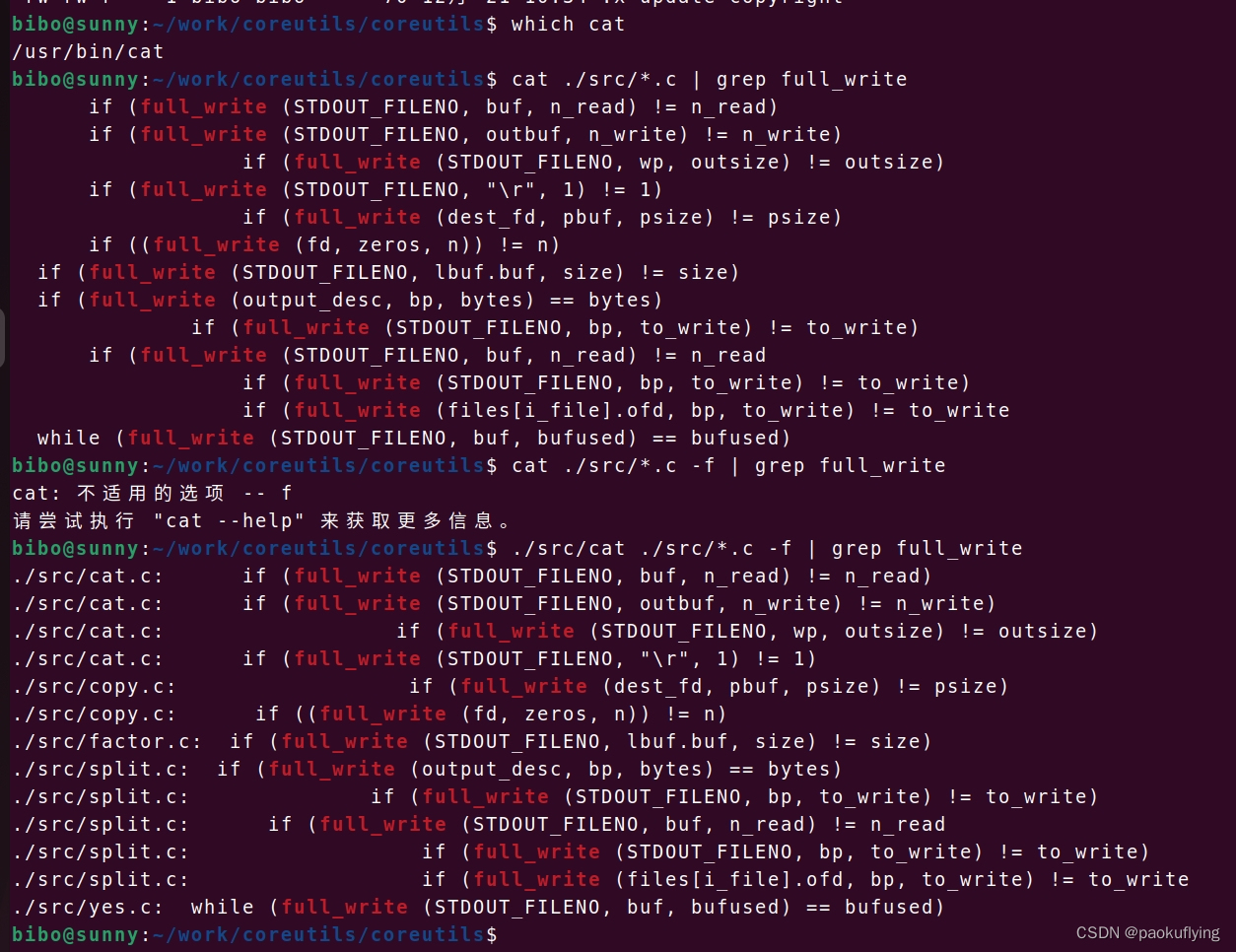
在使用cat命令配合grep批量搜索文件内容时,我仅仅能知道是否搜索到,不知道是在哪个文件里找到的。比如cat ./src/*.c | grep full_write,在src目录下的所有.c文件里找full_write,能匹配到所有的full_write,但是不知道它们分别在哪些文件里。于是我给cat命令增加了一个-f功能,这样能在每一行前面加上文件名,并且加一个冒号':'。这样就能直观的知道它们分别是在哪个文件里找到的,命令为cat ./src/*.c -f | grep full_write。找到之后再配合-n,就能显示出它是在哪个文件的哪一行,cat ./src/x.c -n | grep full_write。
对比效果
拉取项目
git clone https://git.savannah.gnu.org/git/coreutils.git
做出改动的源文件
./src/cat.c
对比改动

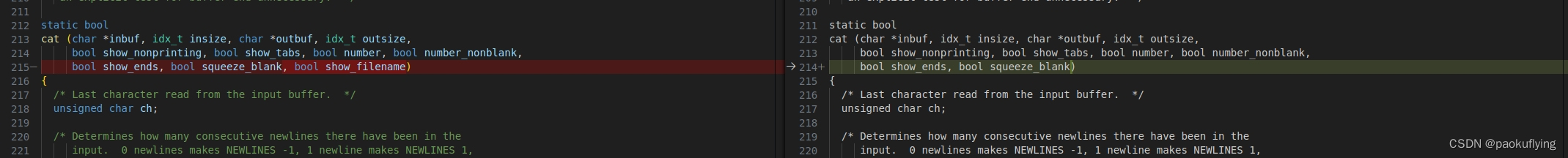

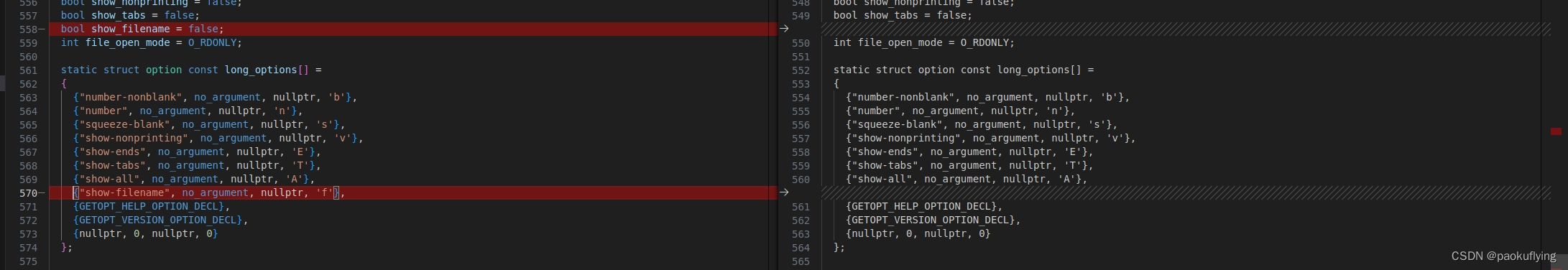



修改后的cat.c文件
/* cat -- concatenate files and print on the standard output.Copyright (C) 1988-2023 Free Software Foundation, Inc.This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modifyit under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published bythe Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or(at your option) any later version.This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty ofMERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See theGNU General Public License for more details.You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public Licensealong with this program. If not, see <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. *//* Differences from the Unix cat:* Always unbuffered, -u is ignored.* Usually much faster than other versions of cat, the differenceis especially apparent when using the -v option.By tege@sics.se, Torbjörn Granlund, advised by rms, Richard Stallman. */#include <config.h>#include <stdio.h>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <sys/types.h>#if HAVE_STROPTS_H
# include <stropts.h>
#endif
#include <sys/ioctl.h>#include "system.h"
#include "alignalloc.h"
#include "ioblksize.h"
#include "fadvise.h"
#include "full-write.h"
#include "safe-read.h"
#include "xbinary-io.h"/* The official name of this program (e.g., no 'g' prefix). */
#define PROGRAM_NAME "cat"#define AUTHORS \proper_name_lite ("Torbjorn Granlund", "Torbj\303\266rn Granlund"), \proper_name ("Richard M. Stallman")/* Name of input file. May be "-". */
static char const *infile;/* Descriptor on which input file is open. */
static int input_desc;/* Buffer for line numbers.An 11 digit counter may overflow within an hour on a P2/466,an 18 digit counter needs about 1000y */
#define LINE_COUNTER_BUF_LEN 20
static char line_buf[LINE_COUNTER_BUF_LEN] ={' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ',' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', '0','\t', '\0'};/* Position in 'line_buf' where printing starts. This will not changeunless the number of lines is larger than 999999. */
static char *line_num_print = line_buf + LINE_COUNTER_BUF_LEN - 8;/* Position of the first digit in 'line_buf'. */
static char *line_num_start = line_buf + LINE_COUNTER_BUF_LEN - 3;/* Position of the last digit in 'line_buf'. */
static char *line_num_end = line_buf + LINE_COUNTER_BUF_LEN - 3;/* Preserves the 'cat' function's local 'newlines' between invocations. */
static int newlines2 = 0;/* Whether there is a pending CR to process. */
static bool pending_cr = false;void
usage (int status)
{if (status != EXIT_SUCCESS)emit_try_help ();else{printf (_("\
Usage: %s [OPTION]... [FILE]...\n\
"),program_name);fputs (_("\
Concatenate FILE(s) to standard output.\n\
"), stdout);emit_stdin_note ();fputs (_("\
\n\-A, --show-all equivalent to -vET\n\-b, --number-nonblank number nonempty output lines, overrides -n\n\-e equivalent to -vE\n\-E, --show-ends display $ at end of each line\n\-n, --number number all output lines\n\-s, --squeeze-blank suppress repeated empty output lines\n\
"), stdout);fputs (_("\-t equivalent to -vT\n\-T, --show-tabs display TAB characters as ^I\n\-u (ignored)\n\-f, --show-filename display filename at begin of each line\n\-v, --show-nonprinting use ^ and M- notation, except for LFD and TAB\n\
"), stdout);fputs (HELP_OPTION_DESCRIPTION, stdout);fputs (VERSION_OPTION_DESCRIPTION, stdout);printf (_("\
\n\
Examples:\n\%s f - g Output f's contents, then standard input, then g's contents.\n\%s Copy standard input to standard output.\n\
"),program_name, program_name);emit_ancillary_info (PROGRAM_NAME);}exit (status);
}/* Compute the next line number. */static void
next_line_num (void)
{char *endp = line_num_end;do{if ((*endp)++ < '9')return;*endp-- = '0';}while (endp >= line_num_start);if (line_num_start > line_buf)*--line_num_start = '1';else*line_buf = '>';if (line_num_start < line_num_print)line_num_print--;
}/* Plain cat. Copy the file behind 'input_desc' to STDOUT_FILENO.BUF (of size BUFSIZE) is the I/O buffer, used by reads and writes.Return true if successful. */static bool
simple_cat (char *buf, idx_t bufsize)
{/* Loop until the end of the file. */while (true){/* Read a block of input. */size_t n_read = safe_read (input_desc, buf, bufsize);if (n_read == SAFE_READ_ERROR){error (0, errno, "%s", quotef (infile));return false;}/* End of this file? */if (n_read == 0)return true;/* Write this block out. */if (full_write (STDOUT_FILENO, buf, n_read) != n_read)write_error ();}
}/* Write any pending output to STDOUT_FILENO.Pending is defined to be the *BPOUT - OUTBUF bytes starting at OUTBUF.Then set *BPOUT to OUTPUT if it's not already that value. */static inline void
write_pending (char *outbuf, char **bpout)
{idx_t n_write = *bpout - outbuf;if (0 < n_write){if (full_write (STDOUT_FILENO, outbuf, n_write) != n_write)write_error ();*bpout = outbuf;}
}/* Copy the file behind 'input_desc' to STDOUT_FILENO.Use INBUF and read INSIZE with each call,and OUTBUF and write OUTSIZE with each call.(The buffers are a bit larger than the I/O sizes.)The remaining boolean args say what 'cat' options to use.Return true if successful.Called if any option more than -u was specified.A newline character is always put at the end of the buffer, to makean explicit test for buffer end unnecessary. */static bool
cat (char *inbuf, idx_t insize, char *outbuf, idx_t outsize,bool show_nonprinting, bool show_tabs, bool number, bool number_nonblank,bool show_ends, bool squeeze_blank, bool show_filename)
{/* Last character read from the input buffer. */unsigned char ch;/* Determines how many consecutive newlines there have been in theinput. 0 newlines makes NEWLINES -1, 1 newline makes NEWLINES 1,etc. Initially 0 to indicate that we are at the beginning of anew line. The "state" of the procedure is determined byNEWLINES. */int newlines = newlines2;#ifdef FIONREAD/* If nonzero, use the FIONREAD ioctl, as an optimization.(On Ultrix, it is not supported on NFS file systems.) */bool use_fionread = true;
#endif/* The inbuf pointers are initialized so that BPIN > EOB, and thereby inputis read immediately. *//* Pointer to the first non-valid byte in the input buffer, i.e., thecurrent end of the buffer. */char *eob = inbuf;/* Pointer to the next character in the input buffer. */char *bpin = eob + 1;/* Pointer to the position where the next character shall be written. */char *bpout = outbuf;while (true){do{/* Write if there are at least OUTSIZE bytes in OUTBUF. */if (outbuf + outsize <= bpout){char *wp = outbuf;idx_t remaining_bytes;do{if (full_write (STDOUT_FILENO, wp, outsize) != outsize)write_error ();wp += outsize;remaining_bytes = bpout - wp;}while (outsize <= remaining_bytes);/* Move the remaining bytes to the beginning of thebuffer. */memmove (outbuf, wp, remaining_bytes);bpout = outbuf + remaining_bytes;}/* Is INBUF empty? */if (bpin > eob){bool input_pending = false;
#ifdef FIONREADint n_to_read = 0;/* Is there any input to read immediately?If not, we are about to wait,so write all buffered output before waiting. */if (use_fionread&& ioctl (input_desc, FIONREAD, &n_to_read) < 0){/* Ultrix returns EOPNOTSUPP on NFS;HP-UX returns ENOTTY on pipes.SunOS returns EINVAL andMore/BSD returns ENODEV on special fileslike /dev/null.Irix-5 returns ENOSYS on pipes. */if (errno == EOPNOTSUPP || errno == ENOTTY|| errno == EINVAL || errno == ENODEV|| errno == ENOSYS)use_fionread = false;else{error (0, errno, _("cannot do ioctl on %s"),quoteaf (infile));newlines2 = newlines;return false;}}if (n_to_read != 0)input_pending = true;
#endifif (!input_pending)write_pending (outbuf, &bpout);/* Read more input into INBUF. */size_t n_read = safe_read (input_desc, inbuf, insize);if (n_read == SAFE_READ_ERROR){error (0, errno, "%s", quotef (infile));write_pending (outbuf, &bpout);newlines2 = newlines;return false;}if (n_read == 0){write_pending (outbuf, &bpout);newlines2 = newlines;return true;}/* Update the pointers and insert a sentinel at the bufferend. */bpin = inbuf;eob = bpin + n_read;*eob = '\n';}else{/* It was a real (not a sentinel) newline. *//* Was the last line empty?(i.e., have two or more consecutive newlines been read?) */if (++newlines > 0){if (newlines >= 2){/* Limit this to 2 here. Otherwise, with lots ofconsecutive newlines, the counter could wraparound at INT_MAX. */newlines = 2;/* Are multiple adjacent empty lines to be substitutedby single ditto (-s), and this was the second emptyline? */if (squeeze_blank){ch = *bpin++;continue;}}/* Are line numbers to be written at empty lines (-n)? */if (number && !number_nonblank){next_line_num ();bpout = stpcpy (bpout, line_num_print);}}/* Output a currency symbol if requested (-e). */if (show_ends){if (pending_cr){*bpout++ = '^';*bpout++ = 'M';pending_cr = false;}*bpout++ = '$';}/* Output the newline. */*bpout++ = '\n';}ch = *bpin++;}while (ch == '\n');/* Here CH cannot contain a newline character. */if (pending_cr){*bpout++ = '\r';pending_cr = false;}/* Are we at the beginning of a line, and filename are requested? */if (newlines >= 0 && show_filename){bpout = stpcpy (bpout, infile);*bpout++ = ':';}/* Are we at the beginning of a line, and line numbers are requested? */if (newlines >= 0 && number){next_line_num ();bpout = stpcpy (bpout, line_num_print);}/* The loops below continue until a newline character is found,which means that the buffer is empty or that a proper newlinehas been found. *//* If quoting, i.e., at least one of -v, -e, or -t specified,scan for chars that need conversion. */if (show_nonprinting){while (true){if (ch >= 32){if (ch < 127)*bpout++ = ch;else if (ch == 127){*bpout++ = '^';*bpout++ = '?';}else{*bpout++ = 'M';*bpout++ = '-';if (ch >= 128 + 32){if (ch < 128 + 127)*bpout++ = ch - 128;else{*bpout++ = '^';*bpout++ = '?';}}else{*bpout++ = '^';*bpout++ = ch - 128 + 64;}}}else if (ch == '\t' && !show_tabs)*bpout++ = '\t';else if (ch == '\n'){newlines = -1;break;}else{*bpout++ = '^';*bpout++ = ch + 64;}ch = *bpin++;}}else{/* Not quoting, neither of -v, -e, or -t specified. */while (true){if (ch == '\t' && show_tabs){*bpout++ = '^';*bpout++ = ch + 64;}else if (ch != '\n'){if (ch == '\r' && *bpin == '\n' && show_ends){if (bpin == eob)pending_cr = true;else{*bpout++ = '^';*bpout++ = 'M';}}else*bpout++ = ch;}else{newlines = -1;break;}ch = *bpin++;}}}
}/* Copy data from input to output using copy_file_range if possible.Return 1 if successful, 0 if ordinary read+write should be tried,-1 if a serious problem has been diagnosed. */static int
copy_cat (void)
{/* Copy at most COPY_MAX bytes at a time; this is min(SSIZE_MAX, SIZE_MAX) truncated to a value that issurely aligned well. */ssize_t copy_max = MIN (SSIZE_MAX, SIZE_MAX) >> 30 << 30;/* copy_file_range does not support some cases, and itincorrectly returns 0 when reading from the proc filesystem on the Linux kernel through at least 5.6.19 (2020),so fall back on read+write if the copy_file_range isunsupported or the input file seems empty. */for (bool some_copied = false; ; some_copied = true)switch (copy_file_range (input_desc, nullptr, STDOUT_FILENO, nullptr,copy_max, 0)){case 0:return some_copied;case -1:if (errno == ENOSYS || is_ENOTSUP (errno) || errno == EINVAL|| errno == EBADF || errno == EXDEV || errno == ETXTBSY|| errno == EPERM)return 0;error (0, errno, "%s", quotef (infile));return -1;}
}int
main (int argc, char **argv)
{/* Nonzero if we have ever read standard input. */bool have_read_stdin = false;struct stat stat_buf;/* Variables that are set according to the specified options. */bool number = false;bool number_nonblank = false;bool squeeze_blank = false;bool show_ends = false;bool show_nonprinting = false;bool show_tabs = false;bool show_filename = false;int file_open_mode = O_RDONLY;static struct option const long_options[] ={{"number-nonblank", no_argument, nullptr, 'b'},{"number", no_argument, nullptr, 'n'},{"squeeze-blank", no_argument, nullptr, 's'},{"show-nonprinting", no_argument, nullptr, 'v'},{"show-ends", no_argument, nullptr, 'E'},{"show-tabs", no_argument, nullptr, 'T'},{"show-all", no_argument, nullptr, 'A'},{"show-filename", no_argument, nullptr, 'f'},{GETOPT_HELP_OPTION_DECL},{GETOPT_VERSION_OPTION_DECL},{nullptr, 0, nullptr, 0}};initialize_main (&argc, &argv);set_program_name (argv[0]);setlocale (LC_ALL, "");bindtextdomain (PACKAGE, LOCALEDIR);textdomain (PACKAGE);/* Arrange to close stdout if we exit via thecase_GETOPT_HELP_CHAR or case_GETOPT_VERSION_CHAR code.Normally STDOUT_FILENO is used rather than stdout, soclose_stdout does nothing. */atexit (close_stdout);/* Parse command line options. */int c;while ((c = getopt_long (argc, argv, "befnstuvAET", long_options, nullptr))!= -1){switch (c){case 'b':number = true;number_nonblank = true;break;case 'e':show_ends = true;show_nonprinting = true;break;case 'n':number = true;break;case 's':squeeze_blank = true;break;case 't':show_tabs = true;show_nonprinting = true;break;case 'u':/* We provide the -u feature unconditionally. */break;case 'v':show_nonprinting = true;break;case 'A':show_nonprinting = true;show_ends = true;show_tabs = true;break;case 'E':show_ends = true;break;case 'T':show_tabs = true;break;case 'f':show_filename = true;break;case_GETOPT_HELP_CHAR;case_GETOPT_VERSION_CHAR (PROGRAM_NAME, AUTHORS);default:usage (EXIT_FAILURE);}}/* Get device, i-node number, and optimal blocksize of output. */if (fstat (STDOUT_FILENO, &stat_buf) < 0)error (EXIT_FAILURE, errno, _("standard output"));/* Optimal size of i/o operations of output. */idx_t outsize = io_blksize (&stat_buf);/* Device and I-node number of the output. */dev_t out_dev = stat_buf.st_dev;ino_t out_ino = stat_buf.st_ino;/* True if the output is a regular file. */bool out_isreg = S_ISREG (stat_buf.st_mode) != 0;if (! (number || show_ends || squeeze_blank)){file_open_mode |= O_BINARY;xset_binary_mode (STDOUT_FILENO, O_BINARY);}/* Main loop. */infile = "-";int argind = optind;bool ok = true;idx_t page_size = getpagesize ();do{if (argind < argc)infile = argv[argind];bool reading_stdin = STREQ (infile, "-");if (reading_stdin){have_read_stdin = true;input_desc = STDIN_FILENO;if (file_open_mode & O_BINARY)xset_binary_mode (STDIN_FILENO, O_BINARY);}else{input_desc = open (infile, file_open_mode);if (input_desc < 0){error (0, errno, "%s", quotef (infile));ok = false;continue;}}if (fstat (input_desc, &stat_buf) < 0){error (0, errno, "%s", quotef (infile));ok = false;goto contin;}/* Optimal size of i/o operations of input. */idx_t insize = io_blksize (&stat_buf);fdadvise (input_desc, 0, 0, FADVISE_SEQUENTIAL);/* Don't copy a nonempty regular file to itself, as that wouldmerely exhaust the output device. It's better to catch thiserror earlier rather than later. */if (out_isreg&& stat_buf.st_dev == out_dev && stat_buf.st_ino == out_ino&& lseek (input_desc, 0, SEEK_CUR) < stat_buf.st_size){error (0, 0, _("%s: input file is output file"), quotef (infile));ok = false;goto contin;}/* Pointer to the input buffer. */char *inbuf;/* Select which version of 'cat' to use. If any format-orientedoptions were given use 'cat'; if not, use 'copy_cat' if itworks, 'simple_cat' otherwise. */if (! (number || show_ends || show_nonprinting|| show_tabs || squeeze_blank || show_filename)){int copy_cat_status =out_isreg && S_ISREG (stat_buf.st_mode) ? copy_cat () : 0;if (copy_cat_status != 0){inbuf = nullptr;ok &= 0 < copy_cat_status;}else{insize = MAX (insize, outsize);inbuf = xalignalloc (page_size, insize);ok &= simple_cat (inbuf, insize);}}else{/* Allocate, with an extra byte for a newline sentinel. */inbuf = xalignalloc (page_size, insize + 1);/* Why are(OUTSIZE - 1 + INSIZE * 4 + LINE_COUNTER_BUF_LEN)bytes allocated for the output buffer?A test whether output needs to be written is done when the inputbuffer empties or when a newline appears in the input. Afteroutput is written, at most (OUTSIZE - 1) bytes will remain in thebuffer. Now INSIZE bytes of input is read. Each input charactermay grow by a factor of 4 (by the prepending of M-^). If allcharacters do, and no newlines appear in this block of input, wewill have at most (OUTSIZE - 1 + INSIZE * 4) bytes in the buffer.If the last character in the preceding block of input was anewline, a line number may be written (according to the givenoptions) as the first thing in the output buffer. (Done after thenew input is read, but before processing of the input begins.)A line number requires seldom more than LINE_COUNTER_BUF_LENpositions.Align the output buffer to a page size boundary, for efficiencyon some paging implementations. */idx_t bufsize;if (ckd_mul (&bufsize, insize, 4)|| ckd_add (&bufsize, bufsize, outsize)|| ckd_add (&bufsize, bufsize, LINE_COUNTER_BUF_LEN - 1))xalloc_die ();char *outbuf = xalignalloc (page_size, bufsize);ok &= cat (inbuf, insize, outbuf, outsize, show_nonprinting,show_tabs, number, number_nonblank, show_ends,squeeze_blank, show_filename);alignfree (outbuf);}alignfree (inbuf);contin:if (!reading_stdin && close (input_desc) < 0){error (0, errno, "%s", quotef (infile));ok = false;}}while (++argind < argc);if (pending_cr){if (full_write (STDOUT_FILENO, "\r", 1) != 1)write_error ();}if (have_read_stdin && close (STDIN_FILENO) < 0)error (EXIT_FAILURE, errno, _("closing standard input"));return ok ? EXIT_SUCCESS : EXIT_FAILURE;
}